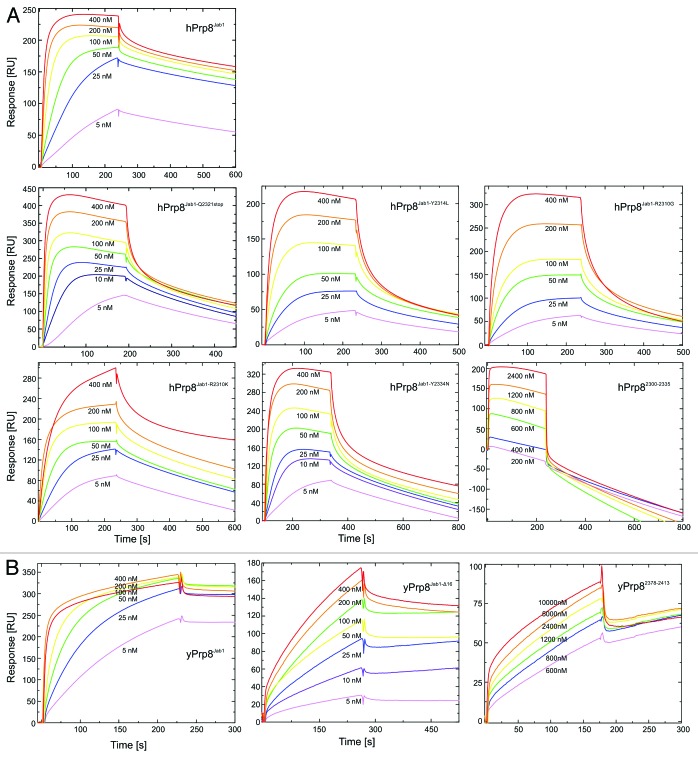
Figure 4. Analysis of Brr2-Prp8 interactions by surface plasmon resonance. (A) Sensorgrams of the interaction of human Brr2 with various human Prp8Jab1 variants (indicated) or a hPrp8 C-terminal peptide (residues 2300–2335). (B) Sensorgrams of the interaction of yeast Brr2 with yeast Prp8Jab1, its tail-deleted variant (yPrp8Jab1-ΔC16) and a yeast Prp8 C-terminal peptide (residues 2378–2413). Concentration ranges of the analytes used are indicated. Proteins and RNAs were produced as described previously.42 N-terminally acetylated peptides comprising the C-terminal 36 residues of hPrp8 (NPKEFYHEVHRPSHFLNFALLQEGEVYSADREDLYA) or yPrp8 (IPLEFYNEMHRPVHFLQFSELAGDEELEAEQIDVFS) and bearing free C-termini were obtained from the Research Group Mass Spectrometry, Leibniz-Institute for Molecular Pharmacology. Surface plasmon resonance analyses were performed using a Biacore 2000 instrument (GE Healthcare) at 20 °C with running buffer containing 10 mM HEPES–NaOH, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 50 µM EDTA, and 0.005% NP40. Flow cells of the Sensor Chip NTA (GE Healthcare) were washed with 20 µl of regeneration solution (350 mM EDTA) and equilibrated using running buffer at 20 µl/min. The second flow cell was activated with 40 µl of 500 µM NiSO4 at 5 µl/min. Human or yeast full-length Brr2, bearing N-terminal His10-tags, were then immobilized on the second flow cell by injecting the proteins at 100 nM in running buffer and at 10 µl/min for 90 s to achieve capture levels of 10 000–12 000 RU. Afterwards, loosely bound proteins were washed away with running buffer. The Jab1 domain variants or peptides were used as analytes in running buffer. Jab1 domain variants and peptides were injected into both flow cells at increasing concentrations (between 5–800 nM for Jab1 variants and between 10–100 µM for peptides) at a flow rate of 30 µl/min. Binding was monitored for 200 s followed by a 300–900 s delay (buffer alone) to monitor dissociation. The sensor surface was regenerated at the end of each binding cycle with 60 µl of regeneration solution at 20 µl/min using the Extraclean feature to remove the immobilized proteins from the surface. Sensorgrams (resonance units vs. time) from the sample cells were corrected by comparison with the sensorgrams from the corresponding control cells and kinetic parameters were extracted using the Biacore 2000 Evaluation Software (GE Healthcare) using a model of 1:1 (Brr2:Jab1 or peptide) binding.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.