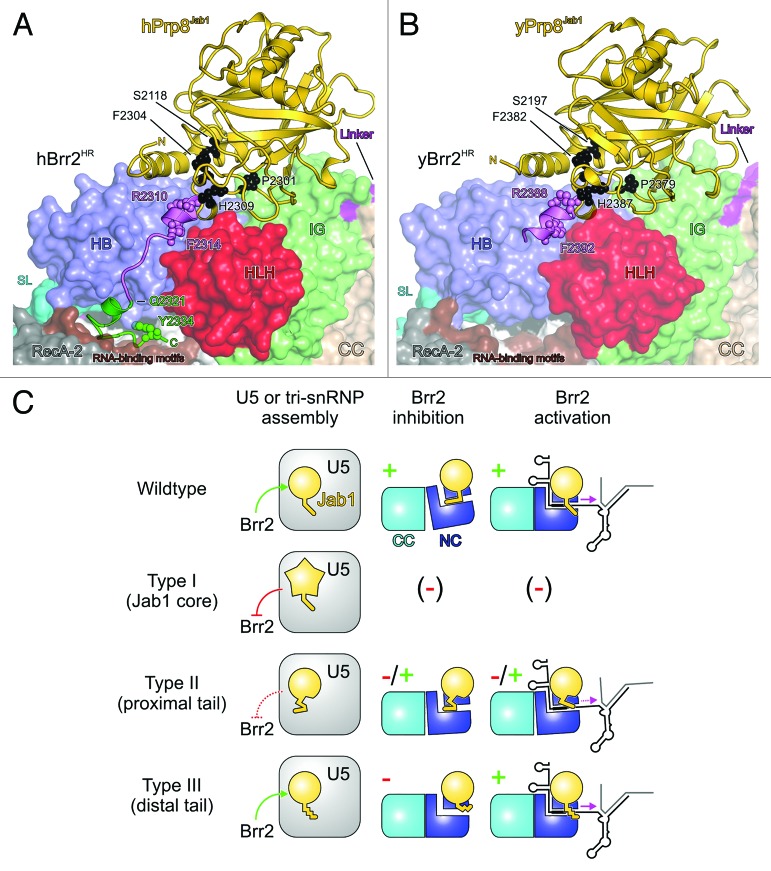
Figure 5. Structural basis for RP13 disease mechanisms. (AandB) Location of human RP13-linked residues (A) and yeast RP13-like residues (B) in the structures of human and yeast Brr2HR–Prp8Jab1 complexes. Brr2 is shown in surface representation. RP13-linked (human) or RP13-like (yeast) residues are shown with small spheres and are labeled. Type I residues/positions, black; type II residues/positions and proximal tail, violet; type III residues/positions and distal tail, green. Other colors as before. (C) Scheme illustrating the phenotypes associated with the various types of RP13-linked/RP13-like mutations. Symbols as in Figure 3. Green arrows or “+” indicate functional processes, red lines or “-“ indicate dysfunctional processes; dashed red lines or “-/+” indicate partial functionality. Brr2 inhibition or activation by Prp8Jab1 variants bearing type I exchanges could not be tested as the proteins were insoluble. However, type I exchanges would be expected to also severely interfere with Brr2 regulation in cases where soluble protein is produced in vivo.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.