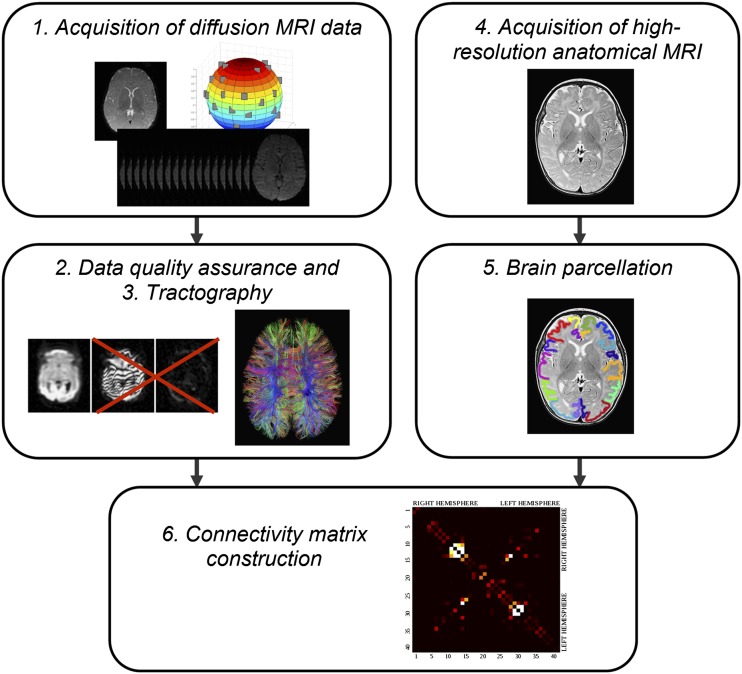
Figure 4.
A typical pipeline for assembling a structural connectome in the developing brain. After a set of diffusion-weighted images is acquired (1), a quality assurance step is performed in which data affected by motion are rejected and the remaining images are corrected for eddy current distortions and affine head motion (2). Although this step may not be necessary in co-operative adults, it is essential for high-quality tractography in infants. The diffusion tensor is calculated for the resulting data and whole-brain streamline fibre tractography is undertaken (3). Commonly, a high-resolution anatomical MRI is acquired (4), which is registered to a standardized brain/atlas that enables automatic brain parcellation into nodes (5). Steps (3) and (5) are combined and the connectivity matrix is constructed (6).