Figure 2. Physical association of the N-terminal domain of AR with BRD4 and its disruption by BET bromodomain inhibition.
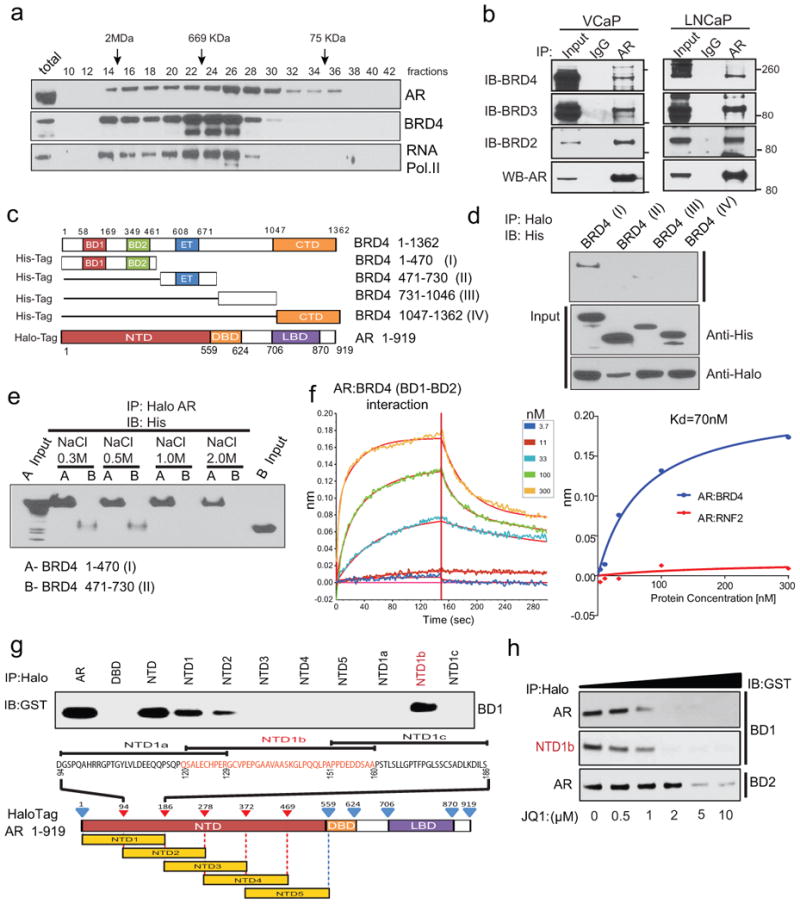
a, VCaP nuclear extracts were fractionated on a Superose-6 column and AR, BRD4 and RNA PolII were analyzed by immunoblotting. b, Endogenous association of AR and BRD2/3/4. VCaP and LNCaP nuclear extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation using an anti-AR antibody. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for the presence of BRD2/3/4 by immunoblotting (upper panel). The immunoblot was stripped and reprobed for AR (lower panel). 5% total lysate was used as input control. c, Schematic of BRD4 and AR constructs used for co-immunoprecipitation experiments. BD1/2, bromodomain 1/2; ET, Extraterminal domain; CTd, C-terminal domain; NTd, N-terminal domain; DBd, DNA-binding domain; LBd, ligand-binding domain. d, N-terminal domain of BRD4 interacts with AR. Proteins from 293T cells co-transfected with various His-tag-BRD4 deletion and Halo-tag-AR constructs were subjected to immunoprecipitation with Halo-beads followed by immunoblotting with His-tag antibody. Inputs are shown in the bottom panel. e, as in d but with the indicated salt concentrations. f, Representative sensorgrams from 3 independent experiments for AR:BRD4 (BD1-BD2) by an OctetRED biolayer interferometry showing direct interaction. Real-time binding was measured by immobilizing biotinylated AR protein on the super streptavidin biosensor and subsequent interaction with varying concentrations of BRD4 (BD1-BD2) protein. The plots show the response versus protein concentration curves derived from the raw binding data. Right, Dissociation constant (Kd) represents the BRD4 (BD1-BD2) concentration yielding half-maximal binding to AR. Protein RNF2 was used as negative control. g, NTD domain of AR interacts with BD1 of BRD4. Equal amounts of in vitro translated proteins were combined and immunoprecipitated using Halo beads followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-GST antibody. h, JQ1 disrupts AR-BD1 interactions. Varying concentrations of JQ1 were incubated with AR-BD1, NTD1b-BD1, AR-BD2 complex prior to immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblot analysis.
