Extended Data Figure 3. Physical association of AR with BRD4 and its disruption by BET bromodomain inhibitor.
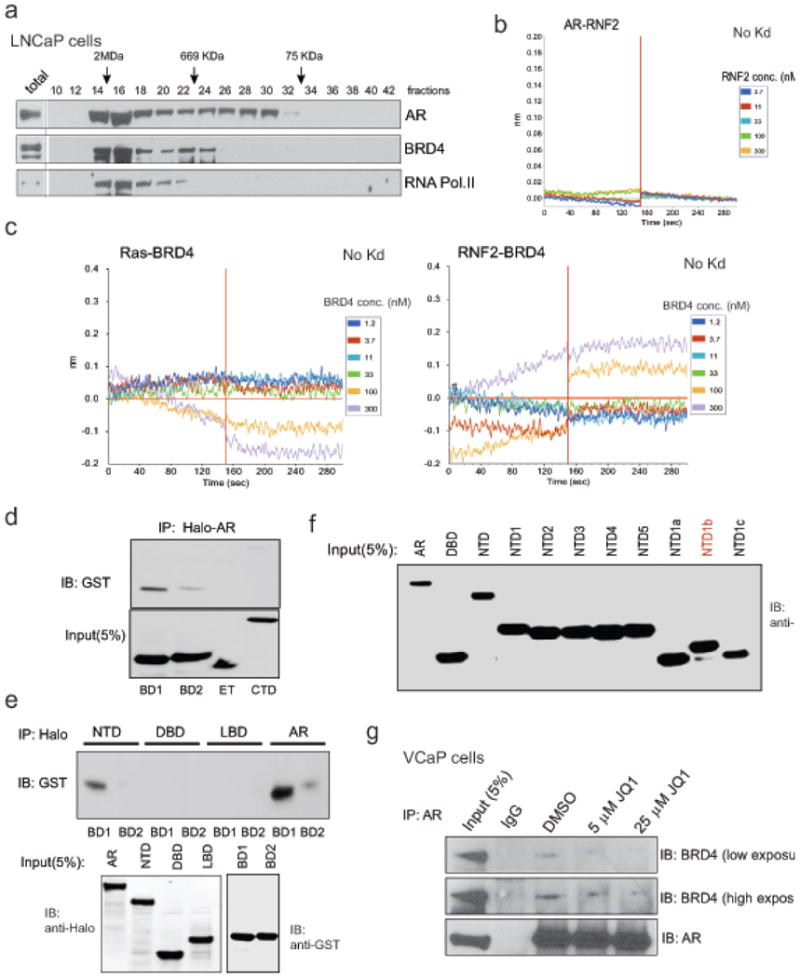
a, LNCaP nuclear extract was fractionated on a Superose-6 column and AR, BRD4 and RNA Pol II were analyzed by immunoblot analysis. b, and c, Representative sensorgrams for AR:RNF2, Ras:BRD4 (BD1-BD2) and RNF2:BRD4 (BD1-BD2) interactions by an OctetRED biolayer interferometry. Real time binding was measured by immobilizing biotinylated AR, Ras or RNF2 proteins separately on a streptavidin biosensor and subsequent interaction with varying concentrations of analyte proteins (RNF2 or BRD4 (BD1-BD2)) individually. Immobilized Ras or RNF2 biosensors did not display binding with BRD4 indicating that the AR-BRD4 interaction is specific. Representative sensorgrams from 4-6 independent experiment are shown. d and e, In vitro binding analysis of AR and indicated domains of BRD4. Equal amounts of in vitro translated full-length Halo-tag-AR protein and GST-tag-BRD4 domains were combined and immunoprecipitated using Halo beads followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-GST antibody. f, JQ1 disrupts the endogenous AR-BRD4 interaction. VCaP cells were treated with JQ1 for 6hrs followed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis as in Figure 2b.
