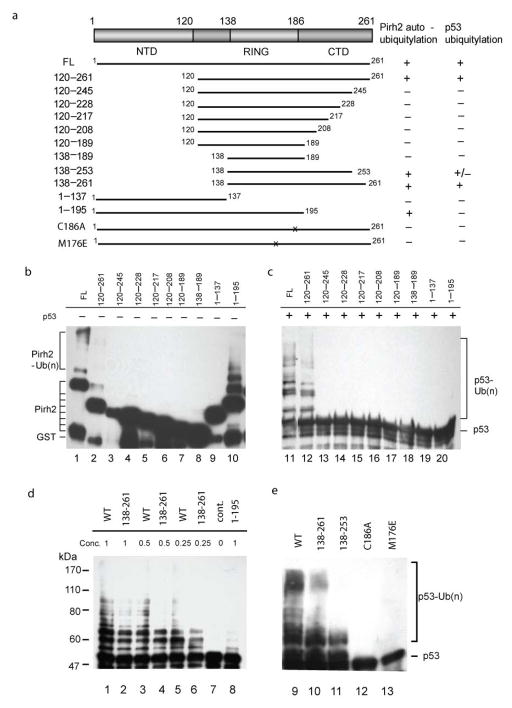
Figure 6.
Assessment of the ubiquitylation activity of Pirh2 deletion mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of the Pirh2 deletion mutants and their activities in auto- and p53-ubiquitylation. (b) Autoubiquitylation (lanes 1–10, left panel) and ubiquitylation of p53 (lanes 11–20, right panel) using different Pirh2 deletion mutants as indicated. The degradation product of the GST-Pirh2 fusions to GST alone is noted (GST). (c) Ubiquitylation of p53 using various concentrations of the wild type Pirh2, the mutants 138–261 and 1–195 as indicated. (d) Ubiquitylation of p53 using the wild type Pirh2, and the mutants 138–261, 138–253, C186A and M176E. All Pirh2 mutants were purified as GST fusions and subjected to the in vitro ubiquitylation assays in the absence (lanes 1–10) and the presence of p53 (lanes 11–20). Autoubiquitylation of the Pirh2 mutants was evaluated by blotting with an antibody against GST. Ubiquitylation of p53 mediated by the Pirh2 mutants was evaluated by blotting with an antibody against p53 (Pab1801).