Figure 1.
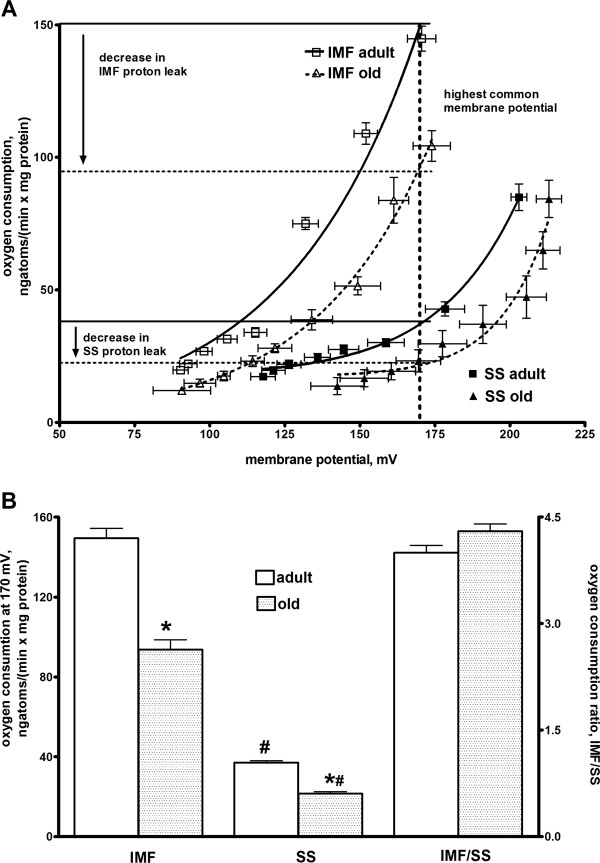
Proton leak in muscle mitochondria from adult and old rats. A: Titration curve of membrane potential against respiration rate during state 4 respiration represents the kinetic response of the proton leak to changes in membrane potential in intermyofibrillar and subsarcolemmal skeletal muscle mitochondria. Non linear regression curve fits show that proton leak was significantly (P < 0.05) lower in subsarcolemmal than in intermyofibrillar mitochondria, and in intermyofibrillar and subsarcolemmal mitochondria from old rats compared to adult rats. B: Oxygen consumption values at the highest common membrane potential (170 mV) and ratio between intermyofibrillar and subsarcolemmal oxygen consumption values at 170 mV in skeletal muscle from adult and old rats. Values are the means ± SEM of eight different rats. IMF = intermyofibrillar; SS = subsarcolemmal. *P < 0.05 compared to adult rats; #P < 0.05 compared to intermyofibrillar mitochondria (non parametric two-way ANOVA).
