Figure 3. Effects of aP2 inhibitor on lipid accumulation, cholesterol efflux and inflammatory responses in macrophages.
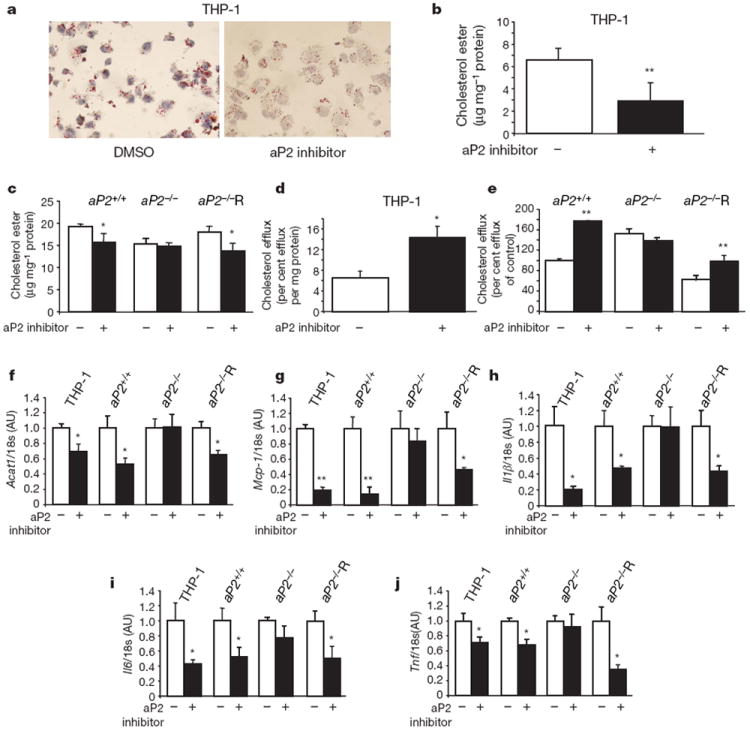
a, Oil Red O staining of THP-1 macrophage foam cells loaded with acetylated low density lipoprotein (50 μg ml−1) in the absence or presence of aP2 inhibitor (25 μM). Magnification, ×400. b, c, Cholesterol ester levels normalized to cellular protein content in human THP-1 macrophages (b) and mouse macrophage cell lines, aP2+/+, aP2−/− and aP2−/−R (c). d, e, APOA1-specific cholesterol efflux in THP-1 macrophages (d) and mouse cell lines (e) in the absence or presence of aP2 inhibitor (25 μM). f–j, Expression of Acat1 (f) and chemoattractant and inflammatory cytokines, Mcp-1 (g), Il1β (h), Il6 (i), and Tnf (j) in macrophages normalized to 18s rRNA levels. Data are normalized to untreated cells and expressed as the mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the control (each untreated cell line). DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide.
