Figure 4. 1-Methylnicotinamide (MNA) serves as a substrate for aldehyde oxidase/GAD-3 to form hydrogen peroxide.
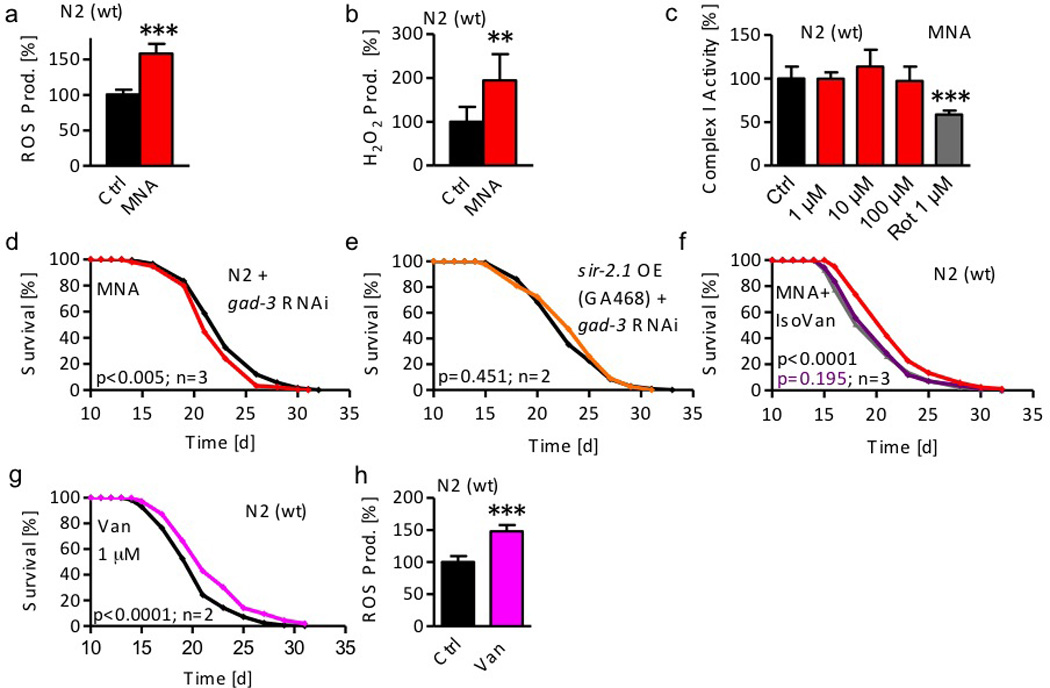
a ROS levels in wild-type (wt) nematodes following exposure to 1 µM MNA for 4 hrs (red bar) compared with untreated nematodes (black bar). b H2O2 production following exposure to 1 µM MNA for 4 hrs. Data represent mean values with standard deviation of at least 2 independent experiments. c Complex I activity after treatment with 1, 10, and 100 µM MNA; the complex I-inhibitor rotenone (1 µM) served as positive control. Data represent mean values with standard deviation of at least 2 independent experiments and n=4 each. Lifespan analyses d of wt nematodes treated with RNAi against gad-3 exposed to 1 µM MNA; e of sir-2.1 overexpressing nematodes (strain GA468) treated with RNAi against gad-3 (orange); f of wt nematodes exposed to MNA (1 µM) in the presence (purple) or absence of IsoVan (red) compared with worms treated with IsoVan only; g of wt nematodes exposed to the AOX1/GAD-3 substrate vanillin (1 µM, pink). h ROS levels in wild-type (wt) nematodes following exposure to 1 µM vanillin for 24 hrs (pink bar) compared with untreated nematodes (black bar). Data represent mean values with standard deviation of 2 independent experiments.
