Figure 13. Fabrication of microfluidic 3D scaffolds with hydrogels.
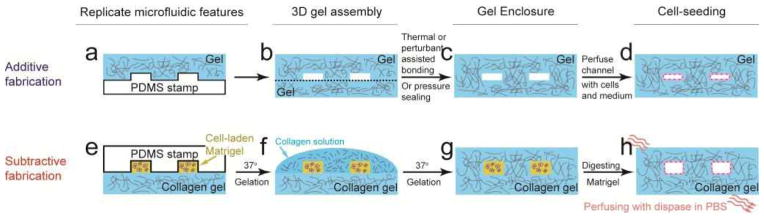
Schematic of the additive (a–d) and subtractive (e–h) fabrications of microfluidic 3D scaffolds with hydrogel biomaterials,[48,279,284] which provided appropriate platforms for studying epithelial/endothelial cell-stromal cell interactions as well as vascular physiology and morphogenesis. In common, both fabrication methods take four steps: (1) using hydrogel precursors to replicate the microfluidic features from a PDMS mold using soft lithography; (2) after gelation, the hydrogel replicate is assembled with other hydrogel substrates, which, if repeated, might eventually achieve a multi-layered 3D hydrogel scaffold; (3) the assembled hydrogel scaffold should be sealed (thermally, chemically or mechanically) before perfusing culture medium and cells; (4) perfusing the microfluidic channels with culture medium and cells. See text for more descriptions.
