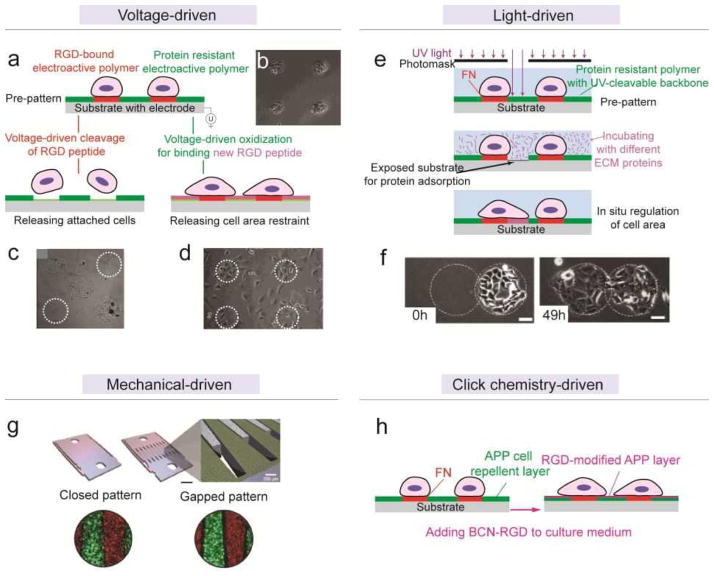
Figure 8. Dynamic regulation of micro/nano-patterns of cell adhesive cues on 2D substrates.
(a) Schematic of using electroactive polymers for voltage-driven dynamic regulation of micro-patterns. See text for detailed description. (b) Phase contrast image of pre-patterned cell clusters.[193] Reproduced with permission from [193]. Copyright 2003, American Chemical Society. (c) Phase contrast image of cell clusters remained after voltage-driven releasing of two other clusters (released clusters were marked by white circles).[194] Reproduced with permission from [194]. Copyright 2006, American Chemical Society. (d) Phase contrast image of cells spreading out after the area outside the original patterns (marked by white circles) were activated by voltage and functionalized with solvent RGD peptides.[193] Reproduced with permission from [193]. Copyright 2003, American Chemical Society. (e) Schematic of light-driven cleavage of cell-repellent polymer coating, rendering in situ modulation of cell adhesion patterns.[202] (f) Phase contrast images showing guided cell migration after releasing neighboring (left circle) cell-repellent coating in situ. Reproduced with permission from [202]. Copyright 2006, Elsevier. (g) Schematic (top) and fluorescent images (bottom) of mechanical-driven modulation of hepatocytes-stromal cells co-culture patterns.[203] Reproduced with permission from [203]. Copyright 2007, United States National Academy of Sciences. (h) Schematic of one-step dynamic regulation of micro-patterns by click chemistry.[204] Solute BCN-RGD reacted with and immobilized onto APP cell-repellent coating and relieved the original restraints on cell adhesion.