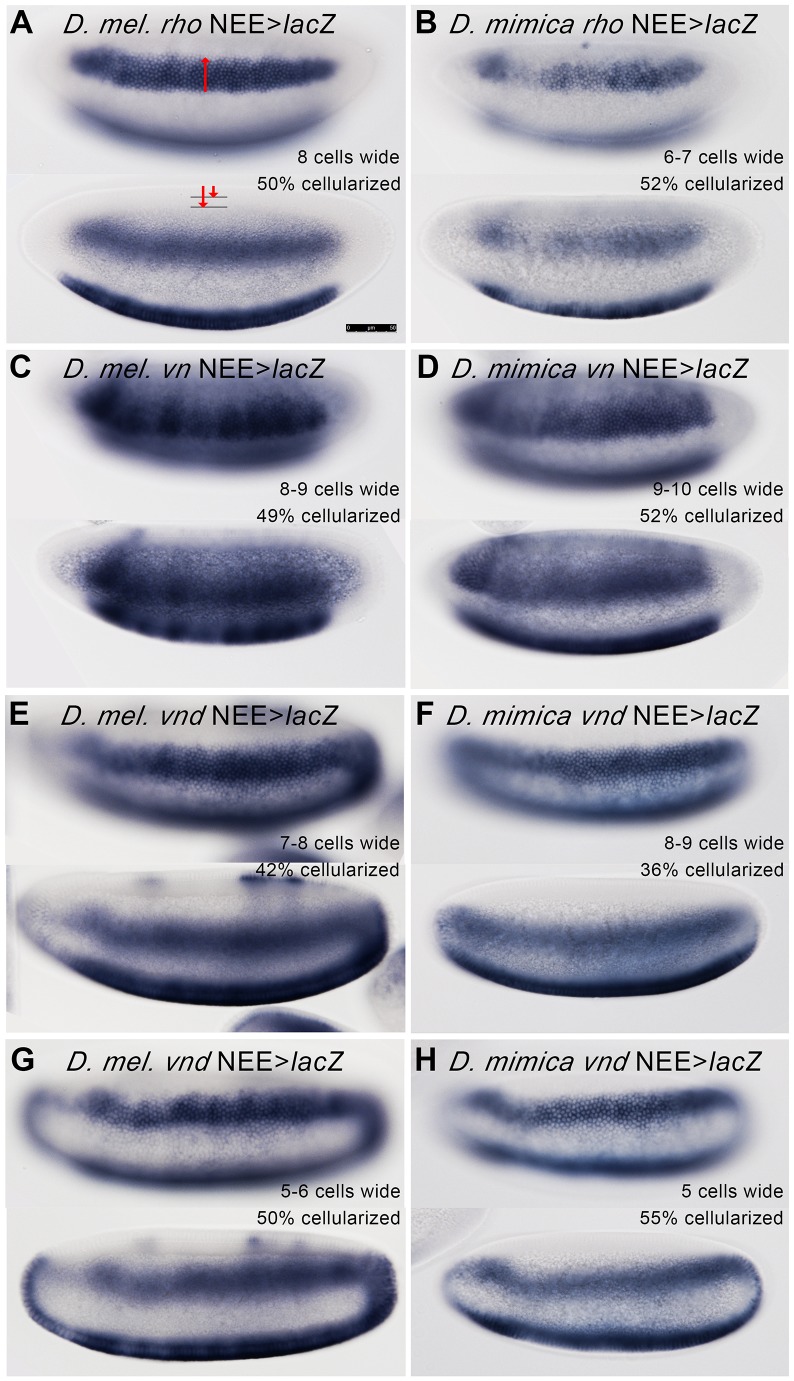
Figure 2. The NEEs from D. mimica Can Drive Expression in Neurogenic Ectoderm of D. melanogaster Despite Replacement of Inter-Element Spacers with MSR.
NEEs from the D. mimica, a member of the Hawaiian modified mouthparts clade, were cloned and tested in D. melanogaster transgenic reporter assays. Expression of the lacZ reporter gene driven from D. melanogaster NEEs (A, C, E, G) and D. mimica NEEs (B, D, F, H) as determined by in situ hybridization with an anti-lacZ probe are shown. In each panel two optical cross-sections are shown. The top image is a surface view allowing determination of the stripe of expression (numbers of cells spanning D/V axis). The bottom image is a cross-section through the dorsal midline allowing determination of the exact stage of embryogenesis (% cellularization as determined at 50% egg length on the dorsal midline). The expression patterns driven by the rho (A, B) and vn (C, D) NEEs are shown for the stages close to 50% cellularization. The expression patterns for the vnd NEEs are shown at two time points: an earlier time point at about ∼40% cellularization (E, F) and a later time point at ∼50% cellularization (G, H). For both Hawaiian and non-Hawaiian vnd NEEs, activity is dorsally repressed by the the Dpp gradient via a conserved binding site for the Shnurri:Mad:Medea complex beginning at about midway through cellularization [19]. All embryos are oriented with anterior pole to the left and dorsal side on top. The 50 micron scale bar shown in (A) is the same for all figures.