Figure 5.
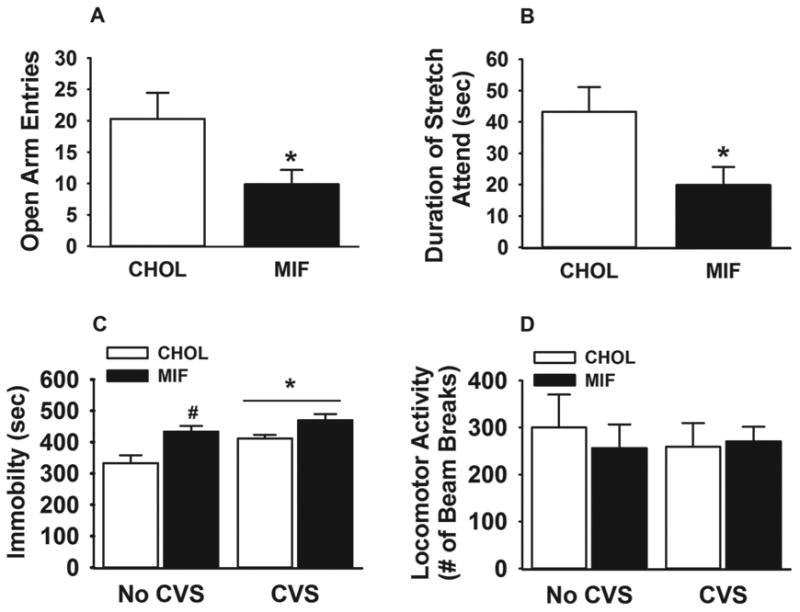
NTS GR inhibition decreases open arm exploration in the EPM and increases helplessness behavior in FST. (A-B) Animals with bilateral mifepristone micropellets in NTS exhibited fewer entries into the open arm of the EPM, and spent less time stretch attending from closed to open arms from closed arm. (C) Both chronic stress exposure and NTS GR inhibition alone increased immobility in the FST. (D) Overall locomotor activity was not affected by bilateral mifepristone implants in the NTS or chronic stress exposure. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n= 8 (mifepristone implanted CVS rats), n=12 (CHOL implanted CVS rats), n=8 (mifepristone implanted no CVS rats), n=12 (CHOL implanted no CVS rats). *p <0.05 vs. CHOL-implanted rats in figure 5 A and B. #p <0.05 vs. no CVS cholesterol in figure 5 C with a main effect of stress.
