Table 1.
Medicinal plants derived phytochemicals with their antiviral activity against HCV core protein.
| PHYTOCHEMICALS | PROPERTIES | CHEMICAL STRUCTURE | FUNCTIONS | REFERENCES |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGCG | Molecular Weight: 458.37172 [g/mol] Molecular Formula: C22H18O11 XLogP3: 1.2 H-Bond Donor: 8 H-Bond Acceptor: 11 |
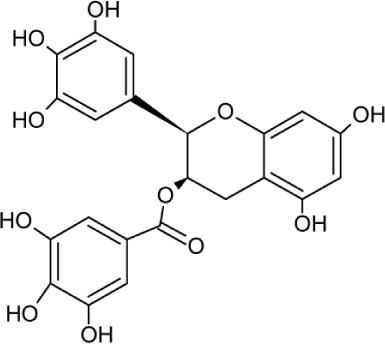
|
Glycoprotein attachment and replication | 30–32 |
| Ladanein | Molecular Weight: 314.28946 [g/mol] Molecular Formula: C17H14O6 XLogP3: 2 H-Bond donor: 2 H-Bond Acceptor: 6 |
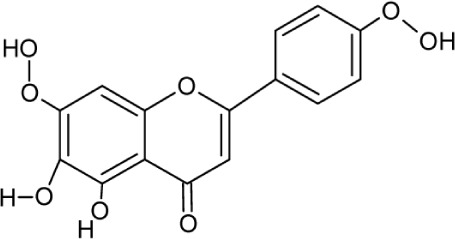
|
HCV entry | 33 |
| Naringenin | Molecular Weight: 272.25278 [g/mol] Molecular Formula: C15H12O5 XLogP3-AA: 2.4 H-Bond donor: 3 H-Bond Acceptor: 5 |
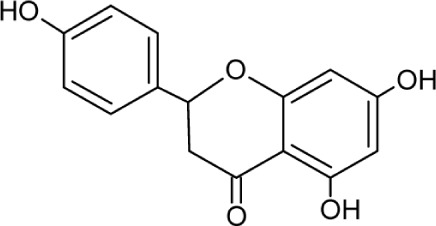
|
Assembly and secretion from core and HCV RNA | 34,35 |
| Silybin | Molecular Weight: 482.43618 [g/mol] Molecular Formula: C25H22O10 XLogP3-AA: 2.4 H-Bond Donor: 5 H-Bond Acceptor: 10 |
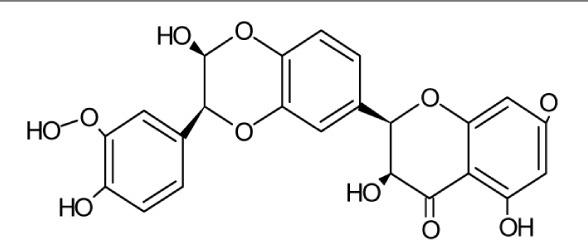
|
Entry, replication, Cell to cell spread of secreted viral proteins | 27–29,36 |
