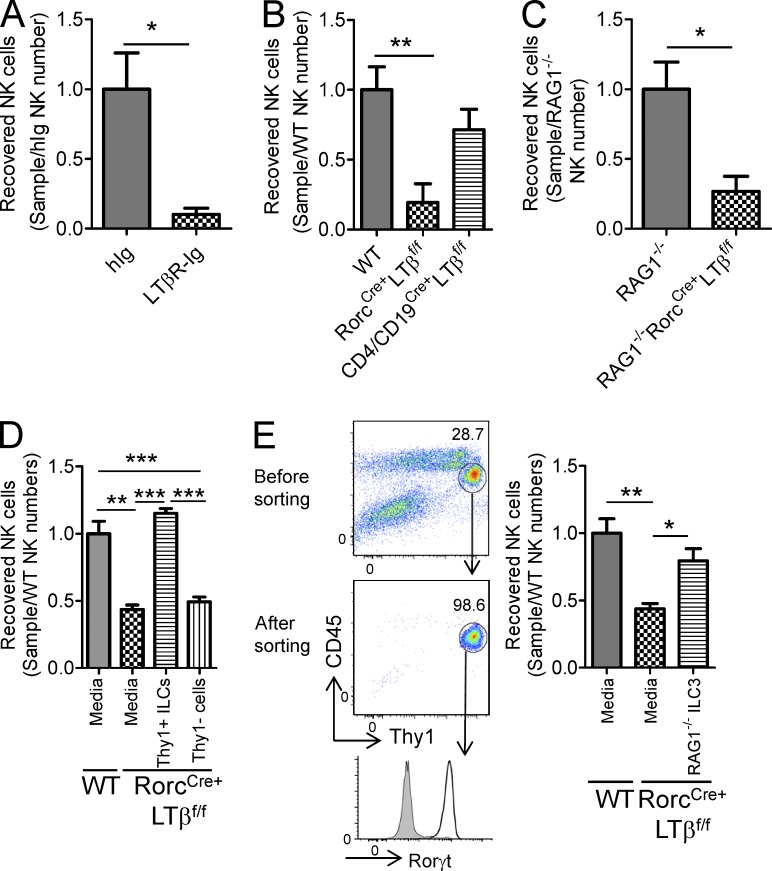
Figure 6.
ILCs could restore defective LT-mediated early NK cell development. Fresh isolated BM cells were cultured without IL-15 cytokine for 10 d and then with 20 ng/ml IL-15 cytokine for an additional 10 d. NK cells were harvested and counted. (A) hIg (n = 4) and LTβR-Ig (n = 4) were added to fresh isolated BM cells from B6 mice at 0, 3, and 6 d. (B and C) BM cells from wild-type, RorcCre+LTβf/f, and CD4/CD19Cre+LTβf/f mice from the B6 (B) or RAG1−/− (C) backgrounds were cultured for 20 d (each group, n = 4). (D) Isolated Lin−, NK1.1−, Thy1+ or Lin−, NK1.1−, Thy1− ILCs from wild-type BM cells were added into the RorcCre+LTβf/f BM culture group at 0 d (each group, n = 4). (E, left) Flow cytometry gating strategy. RORγt+ ILCs from LPLs were isolated from RAG1−/− mice. (right) Isolated RORγt+ ILCs from RAG1−/− intestine LPLs were added into RorcCre+LTβf/f BM cultures at day 0, and recovered NK cells were enumerated on day 20 (each group, n = 3 or 4). Data are representative of three (E) or at least four (A–D) independent experiments. All data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.