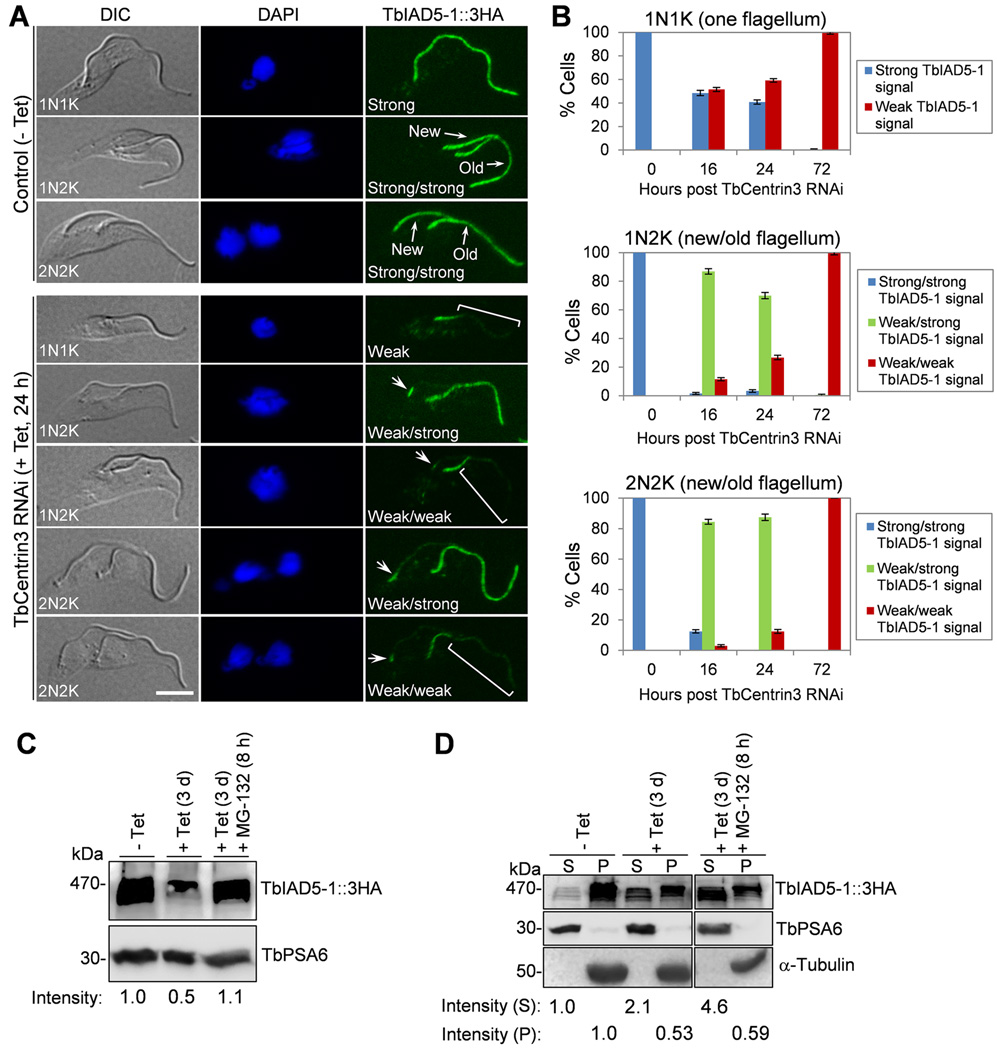
Figure 5. Effect of TbCentrin3 knockdown on the localization and stability of TbIAD5-1.
(A). TbCentrin3 RNAi on TbIAD5-1 localization to the flagellum. Endogenous TbIAD5-1 was tagged with a C-terminal triple HA epitope in cells harboring the TbCentrin3 stem-loop RNAi construct. TbCentrin3 RNAi was induced by tetracycline for 24 h, and cytoskeleton was prepared for immunostaining with FITC-conjugated anti-HA mAb. New and old flagella are indicated. Arrows in TbCentrin3 RNAi cells indicate the TbIAD5-1 signal at the proximal portion of the flagellum. The square brackets outline the portion of flagellum where TbIAD5-1 signal was reduced. For 1N1K cells, strong or weak signal refers to the TbIAD5-1 signal on the single flagellum. For 1N2K and 2N2K cells, strong/strong signal: strong TbIAD5-1 signal on both new and old flagella; weak/strong signal: weak TbIAD5-1 signal on the new flagellum and strong TbIAD5-1 signal on the old flagellum; weak/weak signal: weak TbIAD5-1 signal on both new and old flagella. Bars: 5 µm. (B) Quantitation of control and TbCentrin3 RNAi cells with different intensity of TbIAD5-1 fluorescence signal. Data are presented as the mean percentage ± S.D. of ~300 cells counted from each of the three independent experiments. All cells from the captured images were counted. (C). Effect of TbCentrin3 RNAi on TbIAD5-1 stability. Crude lysate was analyzed by western blotting with anti-HA mAb to detect 3HA-tagged TbIAD5-1. TbPSA6 level served as the loading control. The intensity of the protein bands was determined with ImageJ, and TbIAD5-1 level was normalized with the loading control. (D). Effect of TbCentrin3 RNAi on TbIAD5-1 protein stability in cytosolic and the cytoskeletal fractions. Non-induced control and TbCentrin3 RNAi cells were lysed in PEME buffer containing 1% NP-40 for cytoskeleton preparation. The soluble cytosolic fraction (S) and cytoskeletal pellet fraction (P) were separated by centrifugation, loaded onto a SDS-PAGE gel, and transferred onto a PVDF membrane for western blotting with anti-HA antibody to detect TbIAD5-1::3HA. The cytosolic fraction was detected by anti-TbPSA6, whereas the cytoskeletal fraction was detected by anti-α-tubulin. The intensity of the protein bands was determined with ImageJ as described above. At least three repeats were carried out.