Figure 7.
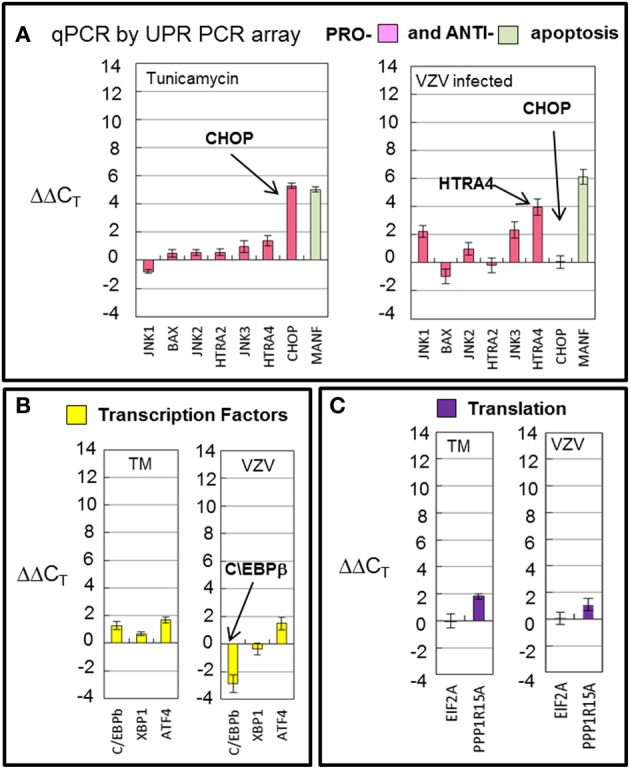
VZV infection downregulated the transcription factor C/EBPb and displayed differential transcription of apoptotic transcripts. Human fibroblast cells (MRC-5) were grown in tissue culture plates then infected with VZV-32 infected MRC-5 cells or treated with tunicamycin (TM), a N-glycosylation inhibitor. At 72 hpi, RNA was processed as described in the legend to Figure 2. (A) Transcription of apoptotic genes differed considerately between VZV infected cells and tunicamycin treated cells. VZV infected cell transcripts showed very fewer CHOP transcripts when compared to TM treatment; infected cells had more transcripts associated with cellular apoptosis such as HTRA4 and MAP kinases JNK1 and JNK3. (B) Transcription of cellular transcription factor C/EBPβ was significantly downregulated in VZV infected cells as compared to the value in TM treated cells (C). There was no difference between VZV vs. TM treatment for two protein translation associated transcripts. Error bars correspond to standard deviation when averaging.
