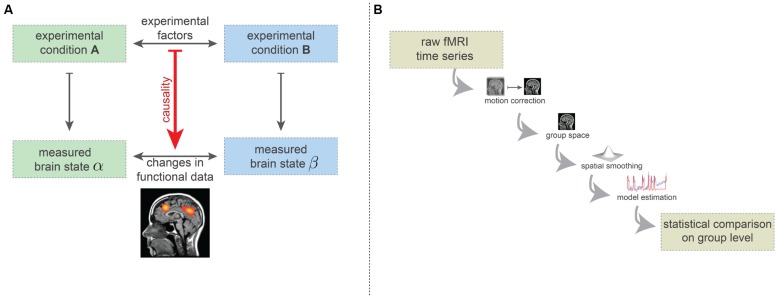
FIGURE 2.
(A) Simplified basic experimental rationale underlying fMRI-based brain-mapping studies. Two (carefully chosen) experimental conditions elicit two distinct brain states. FMRI measurements are able to capture certain aspects of these brain states. The resulting images are compared statistically and this statistical difference is causally ascribed to the difference in terms of experimental factors. (B) Minimalistic preprocessing and data analysis pipelines. Preprocessing includes head-motion correction, transformation into a common coordinate system (e.g., Talairach or MNI space) and spatial smoothing. On this preprocessed data, model estimates are computed (here, we depicted the general linear model). The statistical comparison across the group usually is carried out on basis of the model estimates (e.g., contrasts) and incorporates a correction for the multiple comparisons problem.