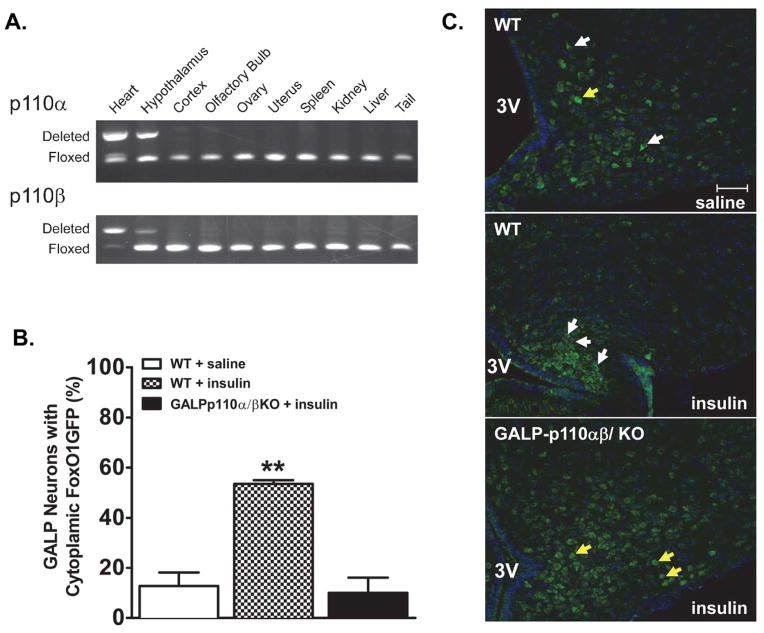
Fig. 1.
The GALP-neuron specific deletion of PI3K catalytic subunits p110α and p110β abolishes the insulin-induced nuclear export of FoxO1GFP within GALP neurons. (A) PCR products showing site of Cre-mediated DNA recombination in tissues from a Cre positive mouse. Deletion of p110α and p110β was detected in the hypothalamus. DNA from the heart of heart-specific p110α/β cKO mouse served as a positive control (first lane [19]). (B) Quantification of FoxO1GFP nuclear translocation in saline-treated WT, insulin-treated WT, and insulin-treated FoxO1GFP-GALP-p110α/β cKO animals (n = 3–4). Subcellular localization of FoxO1GFP is plotted as the percentage of neurons with cytoplasmic FoxO1GFP ** P < 0.001, One-way ANOVA, followed by Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test (C) Subcellular localization of FoxO1GFP in GALP neurons from saline and insulin-treated FoxO1GFP-GALP and FoxO1GFP-GALP-p110α/β cKO animals. After an overnight fast, mice were infused with saline or insulin (100 pmol, 30 min). White and yellow arrows point to GALP neurons with cytoplasmic and nuclear FoxO1GFP localization, respectively. 3V, third ventricle. Scale bar, 50 μm.