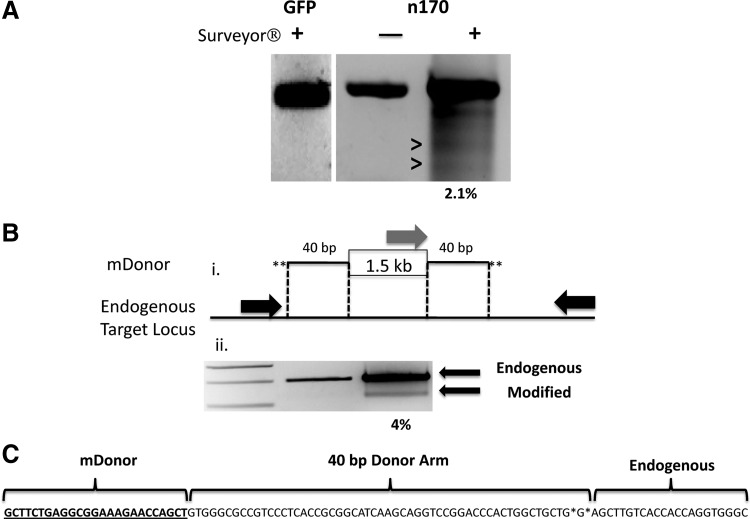
FIG. 6.
Quantitative CoDA-syn IDUA nuclease activity. surveyor nuclease assay for quantification of CoDA-syn nuclease. (A) GFP or CoDA-syn 170 nuclease-treated cells were assayed by amplifying the endogenous IDUA locus. Lanes 1 and 2 show GFP or N170 treated cells±Surveyor that does not show a fragmentation band. Lane 3 is N170-treated cells also treated with Surveyor that shows the generation of fragments (>) consistent with imperfect nonhomologous end joining after nuclease cutting. (B) Minimal donor (mDonor) arm integration and quantification of allele modification. (i) A 1.5-kb plasmid DNA fragment was PCR amplified with primers with phosphorothioate linkages (*) containing an additional 40 bp homologous to the endogenous IDUA locus that flanks the N170 target sequence (dashed lines). (ii) This PCR fragment was cotransfected with the N170 nuclease into 293 cells and a three-primer PCR was performed. The two black primers are unmodified IDUA locus-specific primers that yield an ∼500-bp product (lane 2; and lane 3, upper band). The gray primer is specific for the mDonor and when site-specific integration and allele modification occurs a PCR product of ∼400 bp is observed (lane 3, lower band) Lane 1, molecular weight standards. (C) Minimal donor sequence analysis. Flanking sequence analysis showed a perfect insertion of the mDonor into the IDUA locus. At left is the mDonor sequence, the middle is the 40-bp donor arm, and at right is the endogenous IDUA sequence.