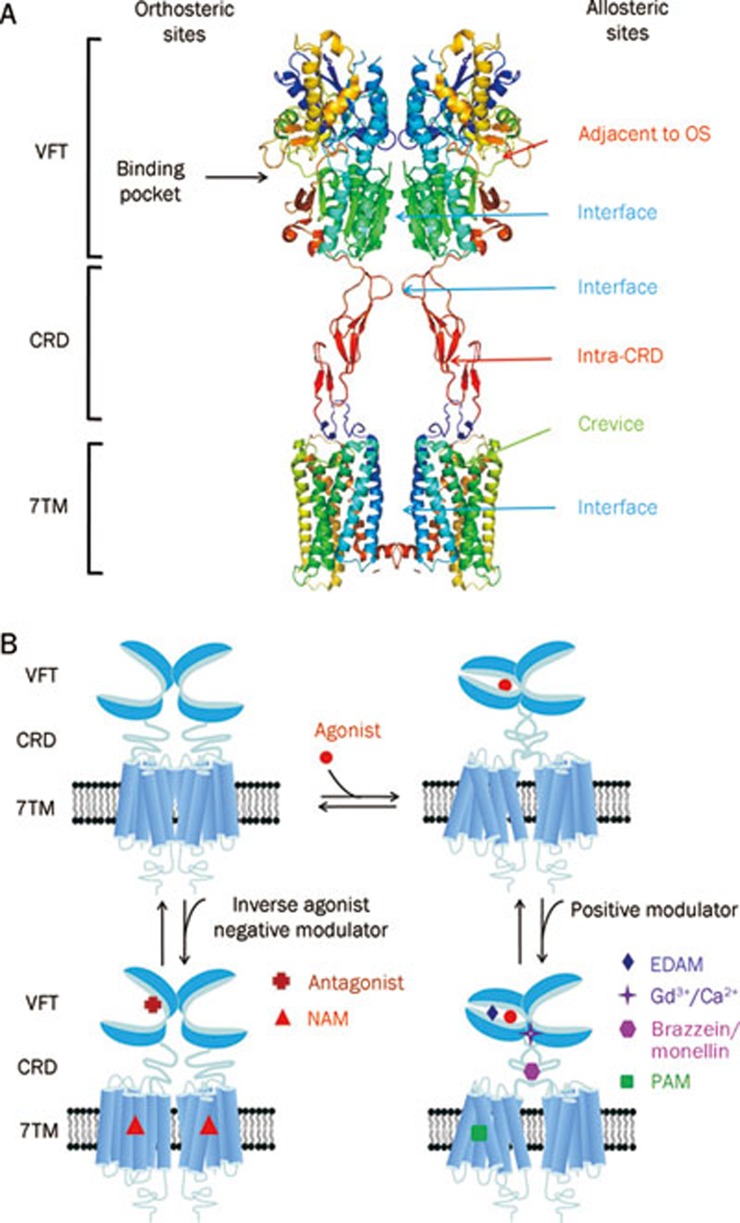
Figure 3.
Great variety of ligands to modulate class C GPCRs function. (A) Schematic model of orthosteric sites and allosteric sites in mGlu-like receptor. There are four groups of allosteric sites in class C GPCR: sites in the 7TM, which have been studied extensively; sites in the extracellular domain including VFT and CRD and sites in the interface between VFT, CRD and 7TM, the latter two open the new possibilities to modulate activity of mGlu receptors. The structure model was built according to the crystal structure of mGlu3 VFT and CRD (PDB ID 2E4W) and the crystal structure of bovine rhodopsin 7TM (PDB ID 1GZM). (B) Modulation mechanism of various ligands on the function of homodimeric class C GPCRs. The orthosteric agonists promote the VFT closure while the antagonists prevent it. The extracellular domain allosteric modulators (EDAM) bind to a site adjacent to the orthosteric site and increase the agonist effect. The Gd3+ ion binds to the interface of the lobe 2 of the VFTs and stabilizes the full active conformation when both VFTs are closed. The sweet proteins brazzein or monellin interact on the CRD of human T1R3 and increase the agonist effect. The typical PAMs or NAMs bind to the 7TM and stabilize the active or inactive conformation of 7TM, respectively.