Fig. 3.
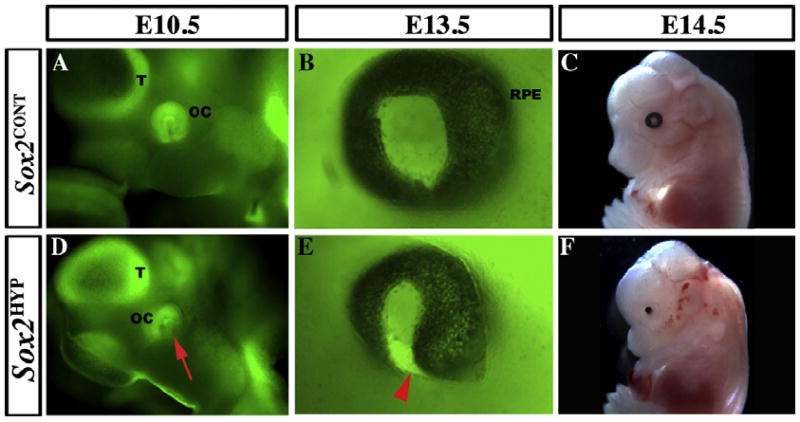
Temporal sequence of the ocular phenotype in whole-mount Sox2HYP embryos. (A and D) Lateral views of E10.5 whole mount Sox2EGFP/+ (A) and Sox2HYP (D) heads. In Sox2EGFP/+ embryos, the ring of the distal optic cup (OC) can be seen ventral and posterior to the telencephalic vesicle (T), contacting the surface ectoderm. The SOX2-positive lens is visible in the center of the ring. In contrast, the ventral aspect of the distal OC is not visible in the Sox2HYP embryo (red arrow, D). (B and E) Lateral views of E13.5 whole mount Sox2EGFP/+ (B) and Sox2HYP (E) eyes. In the Sox2EGFP/+ embryo, the black retinal pigment epithelium surrounds the entire outer surface of the eye. In contrast, the ventral optic fissure of the Sox2HYP eye has failed to close, a defect referred to as coloboma (red arrowhead, E). (C and F) E14.5 whole mount Sox2CONT (C) and Sox2HYP (F) embryos. A round, symmetric eye with a visible lens is present in the Sox2CONT embryo, whereas only a remnant of the retinal pigmented epithelium can be seen in the Sox2HYP embryo.
