Figure 1.
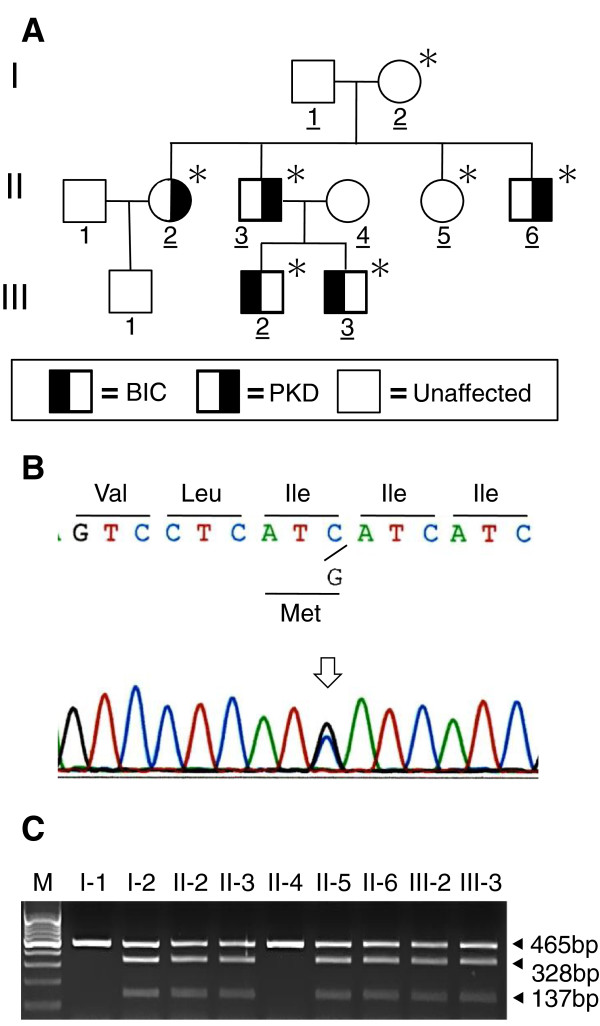
A familial case with benign infantile convulsion and paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia and PRRT2 mutation. A: Affection status for benign infantile convulsion and paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia are as noted. Underlined pedigree numbers denote individuals whose deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was available and who were analyzed in the present study. Asterisks denote PRRT2 mutation carriers. B: Automated DNA sequencing using the polymerase chain reaction product from the patients with either benign infantile convulsion or paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia showed a C-to-G transition at nucleotide 981 in exon 3 of PRRT2 (NCBI accession NM_145239.2), as indicated by the arrow, which resulted in an isoleucine-to-methionine substitution at amino acid position 327 (p.Ile327Met). C. BclI digestion of the exon 3 polymerase chain reaction product showed additional fragments (328bp and 137bp) in two members with benign infantile convulsion (III-2 and III-3) and three members with paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia (II-2, II-3, and II-6) as well as in two unaffected members (I-2 and II-5), which resulted from a C-to-G transition creating a new BclI restriction site. These additional fragments were observed with the wild-type fragment (465bp), confirming the heterozygous mutation. Abbreviations: BIC, benign infantile convulsion; paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia, PKD; bp, base pairs; Val, valine; Leu, leucine; Ile, isoleucine; Met, methionine.
