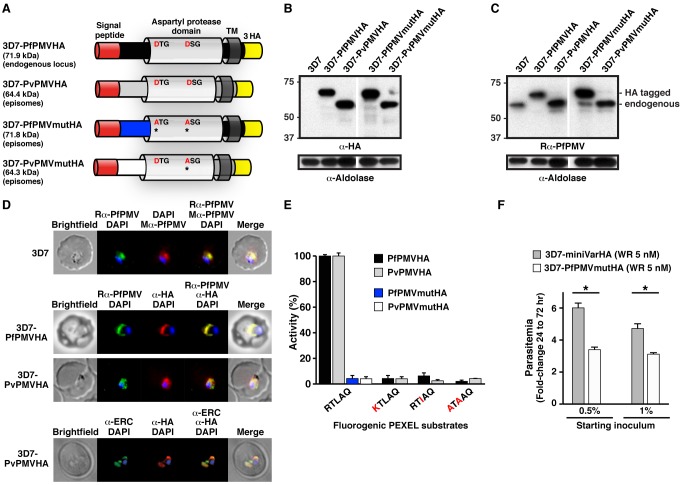
Figure 1. PMV conservation and expression.
(A) Structure and size of PMVHA proteins used in this study. Catalytic dyad residues DTG/DSG are shown including Asp to Ala mutations* in red. TM, transmembrane domain. (B) Immunoblot of infected erythrocytes with α-HA antibodies shows expression of PMVHA proteins in P. falciparum. Sizes indicate that the signal peptides were removed (PfPMVHA, 69.1 kDa; PvPMVHA, 60.9 kDa). (C) Immunoblotting of infected erythrocytes with rabbit α-PfPMV antibodies (Rα-PfPMV) validates they are specific for PfPMV. Endogenous PfPMV is the lower band (lanes 1, 3, 4, 5), and the larger band corresponds to 3× HA-tagged PfPMV (lanes 2, 4). Aldolase is a loading control in (B) and (C) and shows slight overloading of some lanes compared to others. (D, Top) Immunofluorescence micrographs show rabbit α-PfPMV antibodies (Rα-PfPMV, green) label PfPMV in the ER. Colocalizations were performed with mouse α-PfPMV antibodies (Mα-PfPMV, red), shown previously to label PMV in the ER [16]. (Middle) α-HA antibodies (red) label PfPMVHA (Top) and PvPMVHA (Bottom) in the parasite ER. (Bottom) α-HA antibodies (red) label PvPMVHA in the ER, as shown by clocalization with ERC (green). (E) Immunopurified PfPMVHA and PvPMVHA cleave KAHRP peptides containing the PEXEL sequence RTLAQ but not peptides containing point mutations R>K, L>I, or RL>A. Pf and Pv PMVmutHA proteins with catalytic D>A mutations did not cleave the KAHRP RTLAQ peptide. (F) Overexpression of PfPMVmutHA from episomes in P. falciparum 3D7 impairs growth relative to expression of a similar episomal construct encoding a mini PfEMP1HA reporter (miniVarHA). Parasites expressing episomes were selected on 5 nM WR99210 (WR). Two starting inocula were used in triplicate wells, and parasitaemia was determined at 72 h. *p<.0001 (t test). Data are mean ± SEM from duplicate experiments.