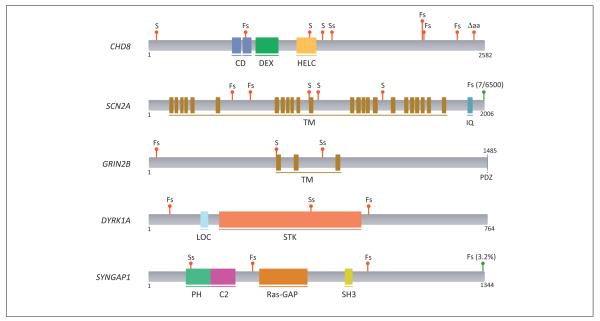
Figure 2.
The location of de novo truncating mutations in the top five autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and intellectual disability (ID) genes. Red markers indicate locations of de novo mutations in ASD and ID cases; green markers indicate locations of truncating mutations in the Exome Sequencing Project (ESP) database of over 6500 samples (see Table 2 for details). Mutation codes: S, stop-gain; Fs, frameshift; Ss, splice-site mutation; ΔAA, amino-acid loss (non-frameshifting). Blocks indicate annotated protein domains from UniProt. Domain names, top to bottom: CD, chromodomain; DEX, helicase ATP-binding; HELC, helicase C-terminal; TM, transmembrane domain; IQ, IQ domain; PDZ, PDZ-binding motif; LOC, bipartite nuclear localization signal; STK, serine/threonine protein kinase; PH, pleckstrin homology domain; C2, C2 domain; SH3, SRC homology 3 domain.