Figure 3.
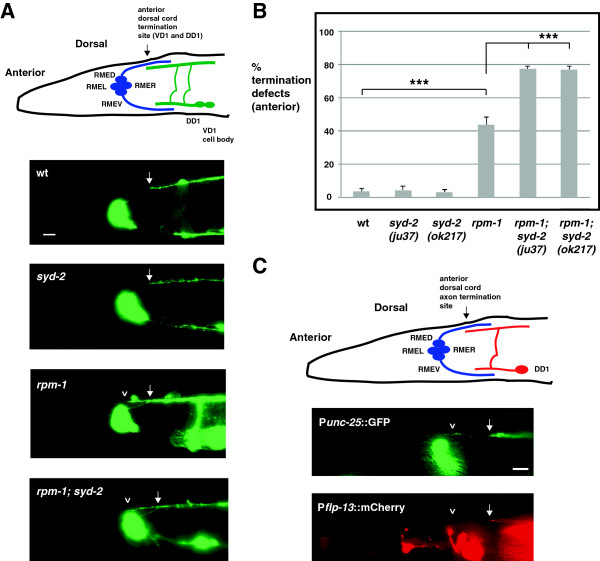
rpm-1 and syd-2 regulate anterior dorsal cord termination. (A) Shown is a schematic of the DD1 and VD1 neurons that fasciculate to form the anterior tip of the dorsal cord, which terminates prior to the RMED axon (arrow) (inspired by Worm Atlas). The anterior tip of the dorsal cord was visualized using Punc-25GFP (juIs76) and epifluorescent microscopy. Highlighted are the normal termination site (arrow), and anterior overextension defects in rpm-1 mutants and rpm-1; syd-2 double mutants (arrowhead). (B) Quantitation of anterior termination defects for the indicated genotypes. For each genotype, the mean is shown from five or more counts (at least 20 worms/count). (C) Punc-25GFP (juIs76) and Pflp-13mCherry (bggIs6) were visualized in rpm-1 mutants using epifluorescent microscopy. Shown is a GFP positive, overextended dorsal cord process (upper panel, arrowhead), and the mCherry positive, anterior termination site of DD1 in a normal location (lower panel, arrow). Analysis was performed on young adults grown at 23°C. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Significance was determined using an unpaired Student’s t test: ***P < 0.001. RMED, dorsal RME neuron; RMEL, left RME neuron; RMER, right RME neuron; RMEV, ventral RME neuron; wt, wild-type. Scale bars, 10 μm.
