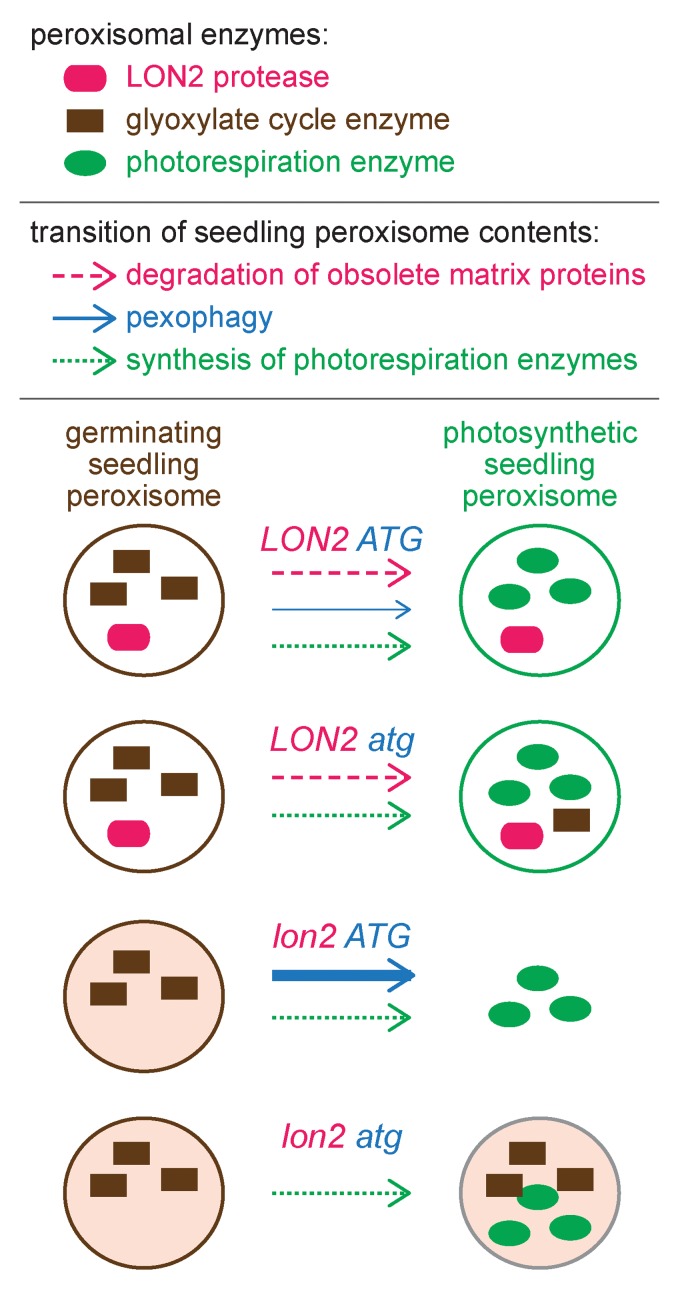
Figure 1. Pexophagy is enhanced when the peroxisomal protease LON2 is dysfunctional. In addition to core peroxisomal proteins, wild-type (LON2 ATG) peroxisomes house glyoxylate cycle enzymes in germinating seedlings and house several photorespiration enzymes in photosynthetic seedlings. When autophagy is prevented (LON2 atg), peroxisomes function normally, but certain glyoxylate cycle enzymes are slightly stabilized, suggesting that pexophagy plays a minor role in degrading seedling peroxisomes. In the lon2 mutant, peroxisomes are present and functional shortly after germination but are sparse and fail to efficiently import matrix proteins in older seedlings. These lon2 defects are fully suppressed by mutating any of several autophagy genes (ATG2, ATG3, or ATG7), suggesting that increased numbers of peroxisomes are targeted for pexophagy when LON2 is mutated. Although lon2 atg double mutant peroxisomes appear to import matrix proteins normally, glyoxylate cycle enzymes are inefficiently degraded, suggesting that LON2 normally promotes turnover of obsolete matrix proteins. The pexophagy trigger in lon2 mutants is not identified.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.