Fig. 1. ALDH2−/− mice have lower levels of serum ALT and hepatic steatosis after ethanol feeding than do WT mice.
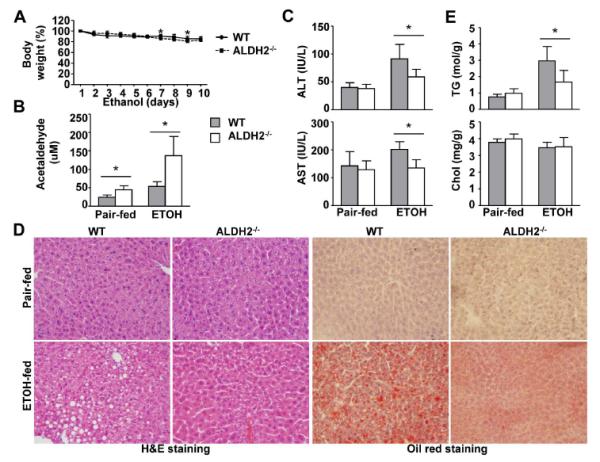
WT and ALDH2−/− mice were fed a control or ethanol diet for 10 days, followed by a single gavage of maltose or ethanol. The mice were euthanized 9 h after gavage. (A) Body weight after ethanol feeding. (B) Hepatic acetaldehyde levels. (C) Serum ALT and AST levels. (D) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and Oil Red O staining of liver tissues. (E) Hepatic triglyceride (TG) and cholesterol (Chol) levels. The values represent means ± SD. (n=4 in pair-fed WT or KO group, n=8 in ethanol-fed WT or KO group) *P < 0.05.
