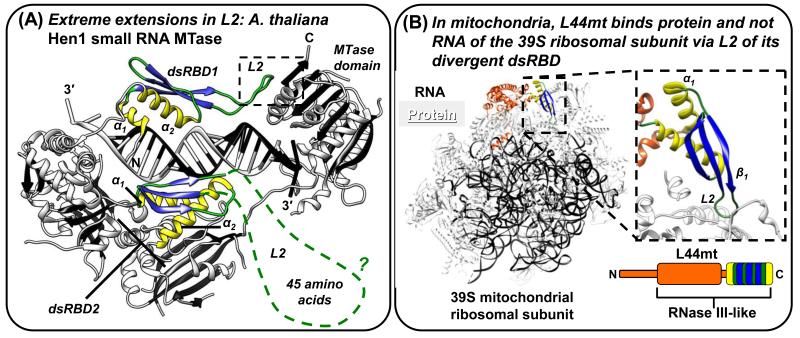
Figure 2. Alterations of L2 that add protein-protein interaction functions to dsRBDs and human STAU1 dsRBD5 as a model type-B dsRBD that has lost dsRNA-binding residues, but retains the dsRBD fold.
(A) X-ray crystal structure of A. thaliana Hen1 small RNA MTase (PDB 3HTX; [52]). The two dsRBDs maintain the color scheme of Figure 1, but the dashed green line of dsRBD2 represents missing L2 electron density, which is an indication of protein disorder. Other protein regions are white with black β-strands, and the dashed box indicates intra-molecular protein interactions between L2 and the MTase domain. (B) The 4.9 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the mammalian (Sus scrofa domesticus; domestic pig) mitochondrial ribosome (PDB 4CE4; [53]) illustrating that the dsRBD domain of RNase III-like L44mt protein, which was modeled with a complete α1-β1-β2-β3-α2 fold, binds ribosomal protein and not RNA. The inset to the right shows the dsRBD-ribosomal protein interactions mediated through L2.