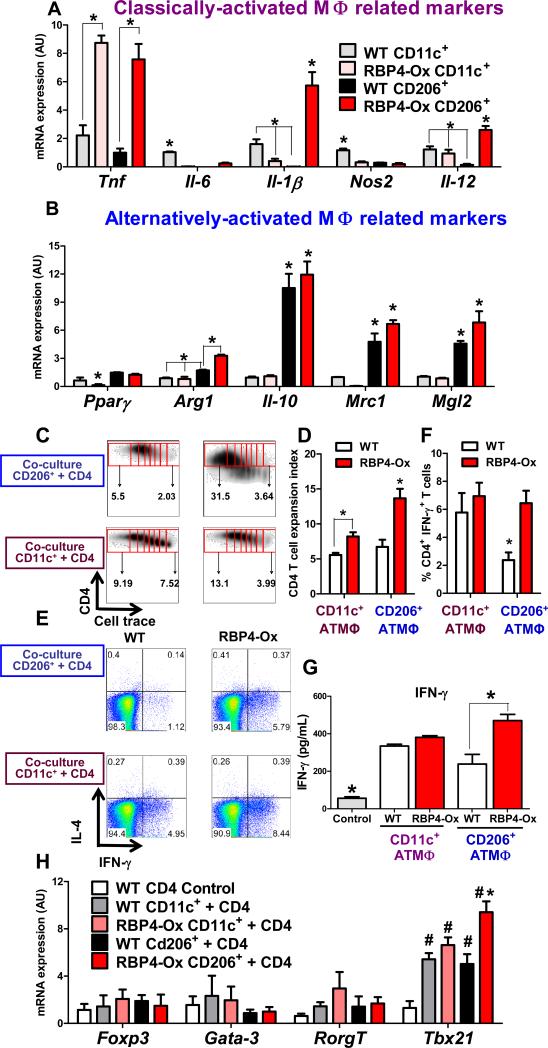
Figure 4. RBP4 overexpression increases proinflammatory markers in CD206+ (alternatively-activated) ATMΦ resulting in Th1 polarization.
mRNA expression of classically-activated (A) and alternatively-activated (B) macrophage-related markers in FACS-sorted (98%-purity) CD11c+ and CD206+ Pg ATMΦ from RBP4-Ox and WT mice (n=3 experiments pooling AT from 10-12 mice/group in each experiment). (C) Flow cytometry representation of CD4 T cell proliferation induced by co-culture with CD11c+ and CD206+ ATMΦ. Proliferation was evaluated by cell trace dilution. (D) Expansion index representing the degree of CD4 T cell proliferation. (E) Flow cytometry representation of IL-4 and IFN-γ intracellular staining in CD4+ T cells co-cultured with CD11c+ or CD206+ ATMΦ. (F) Percentage of IFN-γ+CD4+ T cells in the co-culture assay. (G) IFN-γ levels in media from co-culture of CD11c+ or CD206+ ATMΦ with CD4 T cells. (H) mRNA expression in the co-culture assay of CD4 T cell lineage transcription factors. Co-culture assays were performed with FACS-sorted CD11c+ and CD206+ ATMΦ pooled from 6-10 WT or RBP4-Ox mice and incubated with syngeneic splenic CD4 T cells. Values are means±standard error. *P<0.05 versus all other groups or as indicated. #P<0.05 vs control. Pg: perigonadal.