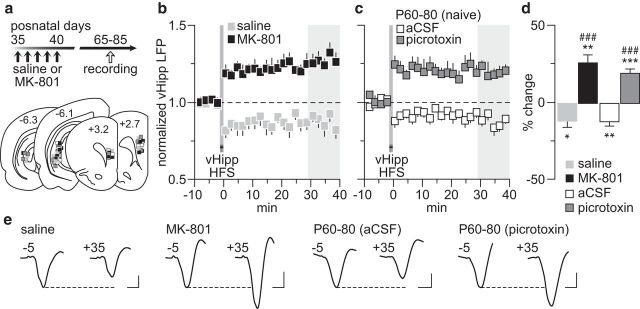
Figure 1.
Disruption of vHipp-induced plasticity in the PFC by early adolescent MK-801 exposure. a, Timeline of the experimental design and summary of the recording sites (PFC: +3.2 to +2.7 mm from bregma) and stimulating sites (vHipp: −6.1 to −6.3 mm from bregma). b, PFC LFP recordings from adult rats (P65–P85) that received saline (n = 10) or MK-801 (n = 9) treatment during early adolescence (P35–40). vHipp HFS resulted in PFC LTD in saline solution controls, whereas an LTP response was observed in MK-801-treated rats. c, PFC infusion of the GABAA antagonist picrotoxin (50 μm/1 μl; n = 11) was sufficient to shift the normal vHipp-induced LTD (aCSF, n = 7) to LTP in adult naive rats (P60–80). d, Summary of the mean LFP response obtained at 30–40 min post-HFS. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005 vs baseline, paired t test. Note that the magnitude of PFC LTP observed in MK-801-treated rats resembles that induced by local PFC infusion of picrotoxin (###p < 0.0005 vs saline solution or aCSF, LSD post hoc test after significant one-way ANOVA; F(3,33) = 28.9; p < 0.0001). e, Example traces of the vHipp-evoked PFC response taken from 5 min pre-HFS (−5) and 35 min post-HFS (+35). Calibration: 4 mV, 20 ms.