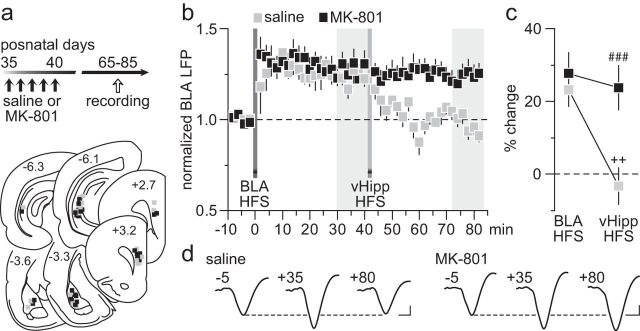
Figure 3.
Early adolescent MK-801 exposure impaired the normal vHipp-dependent depotentiation of BLA-evoked responses in the PFC. a, Timeline of the experimental design and summary of the recording sites (PFC) and stimulating sites (vHipp and BLA). b, Impact of vHipp HFS on BLA-induced LTP in the PFC recorded from adult rats (P65–85) that received saline (n = 8) or MK-801 (n = 9) treatment during early adolescence. Note that the normal vHipp-dependent depotentiation of BLA-LTP is lacking in the PFC of MK-801-treated rats. c, Summary of the mean PFC response obtained at 30–40 min post-HFS. Two-way ANOVA revealed a main effect of treatment (F(1,30) = 10.4, p < 0.005), a main effect of input stimulation (F(1,30) = 9.7, p < 0.005), and a treatment × input stimulation interaction (F(1,30) = 5.4, p < 0.03; ###p < 0.0005 vs saline, ++p < 0.005 vs BLA HFS, LSD post hoc test). d, Example traces of the BLA-evoked PFC response recorded at 5 min pre-BLA HFS (−5), 35 min post-BLA HFS (+35), and 40 min post-vHipp HFS (+80). Calibration: 4 mV, 20 ms.