Figure 1.
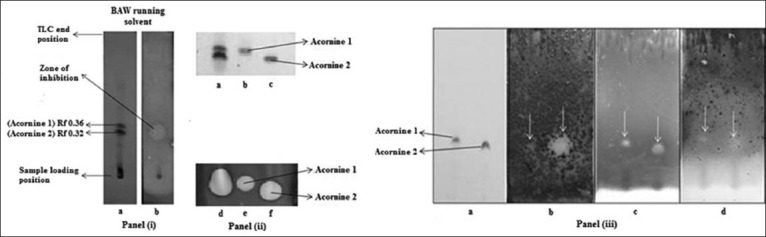
Antifungal activities of A. corniculatum. Panel (i) Lane a -TLC showing Acornine 1 and Acornine 2 in bark extract at Rf 0.36 and 0.32; Lane b - Growth inhibition of S. cerevisiae by Rf 0.36 and 0.32 bands. Panel (ii) -TLC (lanes a, b and c) and bioautography (lanes d, e and f) of bark extract, purified Acornine 1 and Acornine 2 respectively. Panel (iii) a: TLC of purified Acornine 1 and Acornine 2; Panels (iii) b, c and d - bioautography of Acornine 1 and Acornine 2 with T. clypeatus, B. subtilis and B. coagulans respectively. White arrows in Panel (iii) indicate positions of growth inhibitions
