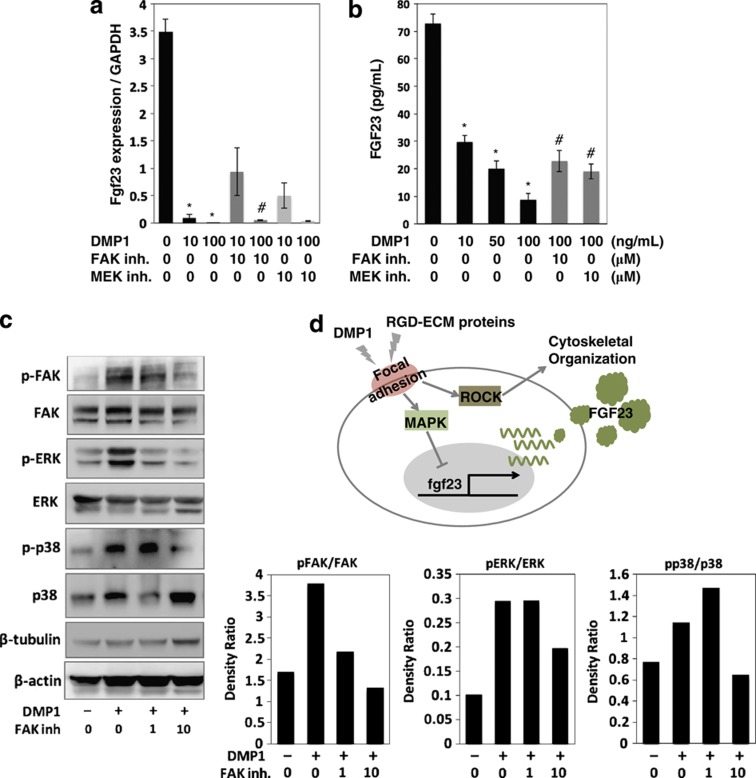
Figure 6.
Effects of DMP1 on the FGF23 production and MAPK signaling in the long-cultured osteoblast cells. (a) Cells were cultured with DMP1 at a concentration of 10 and 100 ng ml−1. After 24 h, total RNA was extracted from the cells, and the expression levels of fgf23 were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR. (b) The secreted protein levels of FGF23 in the cell culture supernatant were determined using ELISA. *Control vs DMP1; #DMP1 vs Inhibitor (inh.), P<0.05. (c) Cells were treated with the FAK inh. in the presence of DMP1. After 24 h, the cell lysates were collected and separated using 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The levels of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated FAK, ERK and p38 were determined using western blotting. The level of β-tubulin and β-actin were evaluated as an internal control. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (d) A possible model for the local regulation of the FGF23 expression by DMP1 and other RGD-containing exracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. Stimulation of DMP1 and RGD-containing ECM proteins to induce focal adhesion formation regulates a broad range of key cellular signals, such as those involved in the MAPK and ROCK pathways. As a result of stimulation with DMP1 and other RGD-containing ECM proteins, the FGF23 expression was downregulated by the MAPK pathway, but not the PI3K or ROCK pathway. In addition, the ROCK pathway is involved in cytoskeletal reorganization. ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; RGD, arginine–glycine–aspartate.