Abstract
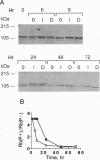
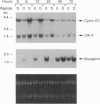
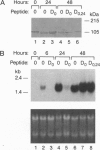
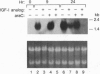
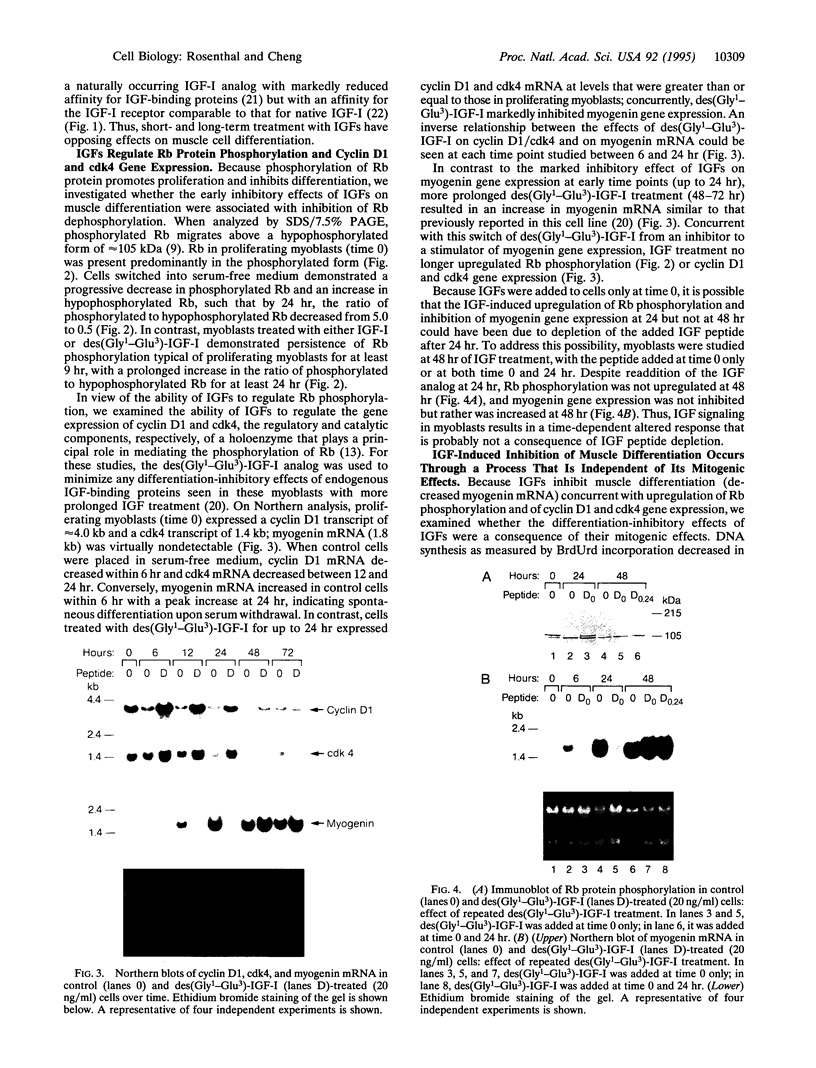
The mechanisms by which insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) can be both mitogenic and differentiation-promoting in skeletal myoblasts are unclear because these two processes are believed to be mutually exclusive in this tissue. The phosphorylation state of the ubiquitous nuclear retinoblastoma protein (Rb) plays an important role in determining whether myoblasts proliferate or differentiate: Phosphorylated Rb promotes mitogenesis, whereas un- (or hypo-) phosphorylated Rb promotes cell cycle exit and differentiation. We hypothesized that IGFs might affect the fate of myoblasts by regulating the phosphorylation of Rb. Although long-term IGF treatment is known to stimulate differentiation, we find that IGFs act initially to inhibit differentiation and are exclusively mitogenic. These early effects of IGFs are associated with maintenance of Rb phosphorylation typical of proliferating cells; upregulation of the gene expression of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and cyclin D1, components of a holoenzyme that plays a principal role in mediating Rb phosphorylation; and marked inhibition of the gene expression of myogenin, a member of the MyoD family of skeletal muscle-specific transcription factors that is essential in muscle differentiation. We also find that IGF-induced inhibition of differentiation occurs through a process that is independent of its mitogenic effects. We demonstrate, thus, that IGFs regulate Rb phosphorylation and cyclin D1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 gene expression; together with their biphasic effects on myogenin expression, these results suggest a mechanism by which IGFs are initially mitogenic and subsequently differentiation-promoting in skeletal muscle.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagley C. J., May B. L., Szabo L., McNamara P. J., Ross M., Francis G. L., Ballard F. J., Wallace J. C. A key functional role for the insulin-like growth factor 1 N-terminal pentapeptide. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):665–671. doi: 10.1042/bj2590665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Francis G. L., Ross M., Bagley C. J., May B., Wallace J. C. Natural and synthetic forms of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and the potent derivative, destripeptide IGF-1: biological activities and receptor binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Edmondson D. G., Li L., Olson E. N. Transforming growth factor beta represses the actions of myogenin through a mechanism independent of DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3822–3826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchkovich K., Duffy L. A., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated during specific phases of the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Scully P., Shew J. Y., Wang J. Y., Lee W. H. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product is modulated during the cell cycle and cellular differentiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Florini J. R. Effects of the somatomedins and insulin on myoblast differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Florini J. R. Relative effects of the somatomedins, multiplication-stimulating activity, and growth hormone on myoblasts and myotubes in culture. Endocrinology. 1980 Feb;106(2):577–583. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-2-577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z., Magri K. A. Hormones, growth factors, and myogenic differentiation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:201–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z., Roof S. L. Insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates terminal myogenic differentiation by induction of myogenin gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 May;5(5):718–724. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-5-718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Magri K. A., Ewton D. Z., James P. L., Grindstaff K., Rotwein P. S. "Spontaneous" differentiation of skeletal myoblasts is dependent upon autocrine secretion of insulin-like growth factor-II. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15917–15923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W., Harwell S. E., Frick K. K. Insulin-like growth factor-I induces cyclin-D1 expression in MG63 human osteosarcoma cells in vitro. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Apr;8(4):510–517. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.4.8052269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Wang N. P., Qian Y. W., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90181-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Schneider J. W., Condorelli G., Kaushal S., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Interaction of myogenic factors and the retinoblastoma protein mediates muscle cell commitment and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90110-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann K. K., Papa V., Brown E. J., Doerries U., Rosenthal S. M., Goldfine I. D. A rapid and simple one step method for isolation of poly(A)+ RNA from cells in monolayer. Endocrinology. 1990 Oct;127(4):2038–2040. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-4-2038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Bradley A., Morris J. H., Edmondson D. G., Venuti J. M., Olson E. N., Klein W. H. Muscle deficiency and neonatal death in mice with a targeted mutation in the myogenin gene. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):501–506. doi: 10.1038/364501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heino J., Massagué J. Cell adhesion to collagen and decreased myogenic gene expression implicated in the control of myogenesis by transforming growth factor beta. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10181–10184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin P., Sejersen T., Ringertz N. R. Recombinant platelet-derived growth factor-BB stimulates growth and inhibits differentiation of rat L6 myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1245–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B. DP and E2F proteins: components of a heterodimeric transcription factor implicated in cell cycle control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;6(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Zhou J., James G., Heller-Harrison R., Czech M. P., Olson E. N. FGF inactivates myogenic helix-loop-helix proteins through phosphorylation of a conserved protein kinase C site in their DNA-binding domains. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1181–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. P., Baker J., Perkins A. S., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. J., Malkowski M., Guo Y., Erickson G. F., Shimasaki S., Ling N. Development of specific antibodies to rat insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBP-2 to -6): analysis of IGFBP production by rat granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1993 Mar;132(3):1176–1183. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.3.7679972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montarras D., Pinset C., Pérez M. C., Ilan J., Gros F. Muscle differentiation: insulin-like growth factors as positive modulators of myogenic regulatory genes? C R Acad Sci III. 1993 Sep;316(9):1025–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Hanaoka K., Hayasaka M., Esumi E., Li S., Nonaka I., Nabeshima Y. Myogenin gene disruption results in perinatal lethality because of severe muscle defect. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):532–535. doi: 10.1038/364532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal-Ginard B. Commitment, fusion and biochemical differentiation of a myogenic cell line in the absence of DNA synthesis. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):855–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. Interplay between proliferation and differentiation within the myogenic lineage. Dev Biol. 1992 Dec;154(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90066-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Sternberg E., Hu J. S., Spizz G., Wilcox C. Regulation of myogenic differentiation by type beta transforming growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1799–1805. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. S., Chu C., Kohtz D. S. Ectopic expression of cyclin D1 prevents activation of gene transcription by myogenic basic helix-loop-helix regulators. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5259–5267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen G. D., Sanes J. R., LaChance R., Cunningham J. M., Roman J., Dean D. C. Roles for the integrin VLA-4 and its counter receptor VCAM-1 in myogenesis. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1107–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90633-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S. M., Brunetti A., Brown E. J., Mamula P. W., Goldfine I. D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I receptor expression during muscle cell differentiation. Potential autocrine role of IGF-II. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1212–1219. doi: 10.1172/JCI115121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Gu W., Zhu L., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Reversal of terminal differentiation mediated by p107 in Rb-/- muscle cells. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1467–1471. doi: 10.1126/science.8197461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman L. A., Cheng Z. Q., Hsiao D., Rosenthal S. M. Skeletal muscle cell-derived insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins inhibit IGF-I-induced myogenesis in rat L6E9 cells. Endocrinology. 1995 Feb;136(2):720–726. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.2.7530651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skapek S. X., Rhee J., Spicer D. B., Lassar A. B. Inhibition of myogenic differentiation in proliferating myoblasts by cyclin D1-dependent kinase. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1022–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.7863328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizz G., Roman D., Strauss A., Olson E. N. Serum and fibroblast growth factor inhibit myogenic differentiation through a mechanism dependent on protein synthesis and independent of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9483–9488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Lajara R., McCusker R. H., Clemmons D. R., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in muscle development. Expression of IGF-I, the IGF-I receptor, and an IGF binding protein during myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13810–13817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Sadow J. L., Rotwein P. Coordinate expression of insulin-like growth factor II and its receptor during muscle differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1543–1547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turo K. A., Florini J. R. Hormonal stimulation of myoblast differentiation in the absence of DNA synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):C278–C284. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.5.C278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]