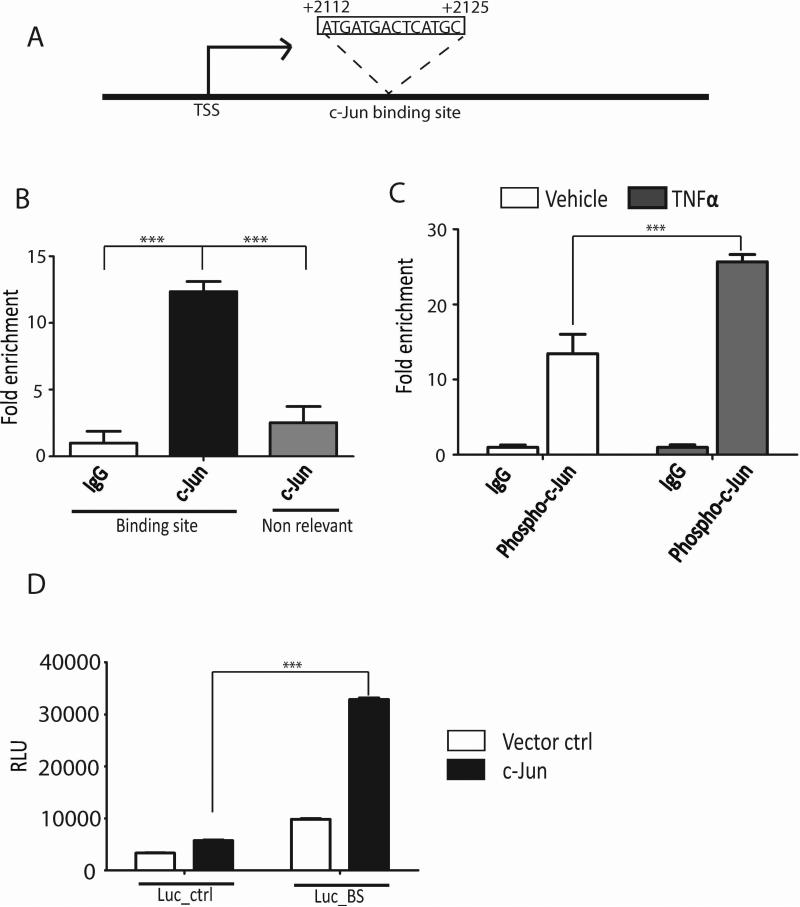
Figure 4. c-Jun binds to ERK3 gene promoter and regulates its transcriptional activity.
(A). A canonic c-Jun binding site exists in intron 1 of ERK3 gene, which presumably functions as a transcription enhancer. TSS: transcription start site. (B). c-Jun is bound to ERK3 gene promoter in HUVECs. ChIP assays were performed using either a c-Jun Ab or goat IgG. The occupancy of c-Jun protein on ERK3 gene promoter region containing the canonic c-Jun binding site or on a non-relevant region was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR and presented as the percentage of sheared chromatin input. (C). TNF-α enhances the binding of phosphorylated c-Jun to ERK3 gene promoter. HUVECs were stimulated with TNF-α or vehicle control. ChIP assays were performed as shown in (B) except that a phospho-c-Jun Ab was used to analyze the occupancy of phosphorylated c-Jun on ERK3 gene promoter. (D). Luciferase assays in HUVECs transfected with either the pGL3-promoter luciferase vector control (Luc-ctrl) or the pGL3-promoter luciferase plasmid incorporated with the c-Jun binding site from ERK3 gene promoter (Luc-BS), together with c-Jun plasmid or the empty vector control (Vector ctrl). Luciferase activity is represented as relative luciferase units (RLU) on the Y-axis.