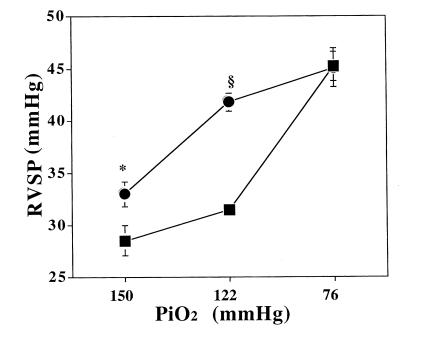
Figure 1.
Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP; mean ± SEM) as an estimate of pulmonary artery systolic pressure in eNOS–/– (closed circles) vs. control (+/+) (closed squares) mice measured after exposure to conditions equivalent to sea level (PiO2 = 150 mmHg), 5,280-ft elevation (PiO2 = 122 mmHg), and 17,000-ft elevation (PiO2 = 76 mmHg). eNOS–/– mice had mildly increased pulmonary pressures at sea-level conditions (*P = 0.013; n = 6 and 9, respectively) and pronounced pulmonary hypertension at modest hypoxia (5,280-ft elevation) (§P < 0.0001; n = 6 and 8, respectively). Severe hypoxia results in similar degrees of pulmonary hypertension in eNOS–/– and control mice (P = ns; n = 7 and 8, respectively). eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase.