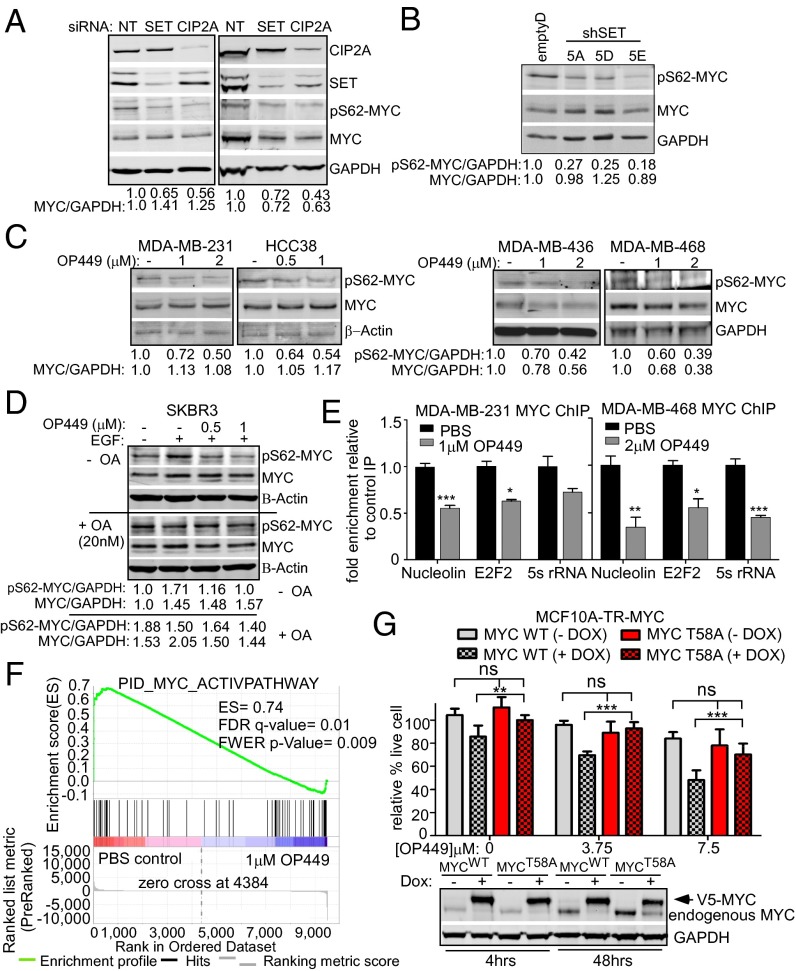
Fig. 5.
OP449 decreases S62-phosphorylated MYC and MYC transcriptional activity contributing to cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells. (A) Western blot analysis of pS62-MYC and MYC proteins in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 cells after siRNA knockdown of SET or CIP2A. The levels of pS62-MYC and total MYC were quantified on a LICOR scanner and calculated over GAPDH. (B) Western blot analysis of pS62-MYC and MYC protein in MDA-MB-231 stable clones with control or SET knockdown (shown in Fig. S3B). (C) Western blot analysis of pS62-MYC and MYC after treatment of the indicated cells with OP449 for 4 h. (D) Western blot analysis of pS62-MYC and MYC from SKBR3 cells starved for 24 h and then treated with OP449 without or with 20 nM okadaic acid (OA) for 2 h, followed by 10 min EGF (100 ng/mL) treatment. (E) qChIP for MYC at the Nucleolin, E2F2, and 5s rRNA promoters after 24 h of treatment with OP449. The fold enrichment of bound DNA was graphed as the fold enrichment in MYC IP relative to the fold enrichment in IgG control IP. (F) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of a MYC gene signature (30) in RNA-seq data from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 1 µM OP449 or PBS for 12 h. The positive enrichment score (ES) and statistical values are listed. (G) MTS assay for MCF10A-TR-MYC cells treated with 1 µg/mL doxycycline (Dox) for 4 h to induce ectopic expression of wild-type (MYCWT) or mutant MYC (MYCT58A). Cells were then treated with different concentrations of OP449 as indicated for 48 h. Representative Western blot of ectopic MYC in these cells with 4 or 48 h of Dox treatment. Error bars represent SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.