Figure 2.
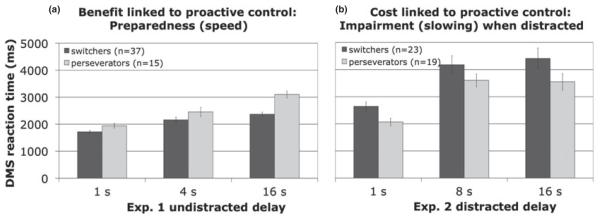
(a) Benefits associated with proactive control (Experiment 1): Flexible task-switchers were faster than perseverators on a working memory task, particularly as working memory demands increased with delay. (b) Costs associated with proactive control (Experiment 2): Flexible task-switchers were slower than perseverators on a working memory task, when a distractor task made it challenging to actively maintain information during the delay.
