Extended Data Figure 8. Formation of apoptotic bodies but not string-like apoptopodia structures is dependent on actomyosin contraction.
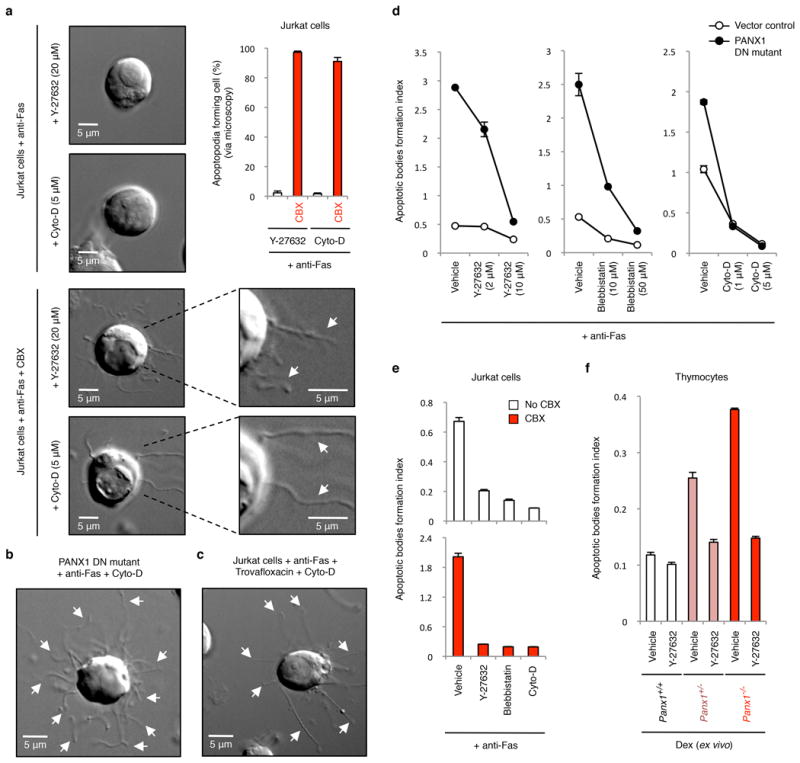
a, Time-lapse images monitoring apoptotic cell morphology of cells treated with or without CBX (500 μM) and in the presence of actomyosin contraction inhibitors. Top right, percentage of apoptotic cells forming string-like apoptopodia structures (387, 414, 459 and 372 apoptotic cells were analysed for Y-27632, Y-27632+CBX, Cyto-D and Cyto-D+CBX-treated cells, respectively, from three independent experiments). b,c, Time-lapse images monitoring apoptotic cell morphology of cells stably expressing the dominant-negative PANX1 mutant (PANX DN mutant) (b) or treated with 40 μM trovafloxacin (c) in the presence of Cyto-D (5 μM). d, Inhibitors of blebbing, Y-27632, blebbistatin, or cytochalasin D (Cyto-D) reduce the formation of apoptotic bodies in Jurkat cells expressing PANX1 DN mutant (n=3). e, Generation of apoptotic bodies by dying cells treated with Y-27632 (10 μM), blebbistatin (50 μM) and Cyto-D (5 μM). Cells were induced to undergo apoptosis in the presence or absence of CBX (500 μM) (n=3). f, The enhanced formation of apoptotic bodies in apoptotic thymocytes from mice with PANX1 deficiency is also blunted by the ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 (10 μM) that blocks membrane blebbing (n=3). Error bars represent s.e.m. Scale bars represent 5 μm. Arrows, apoptopodia.
