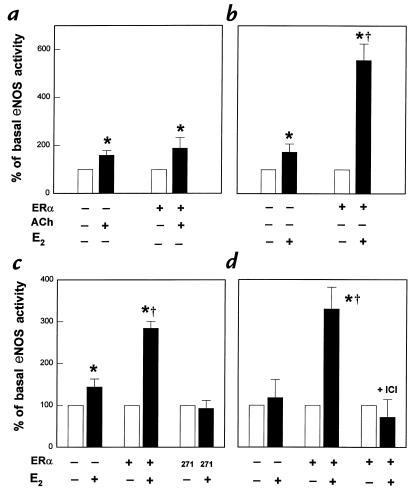
Figure 3.
Specificity of the augmentation of eNOS activation by ERα overexpression. (a and b) Comparison of the effects of ERα overexpression on acute eNOS activation by acetylcholine (ACh) and E2. PAEC were transiently transfected with sham plasmid or with ERα cDNA. After 72 h, [3H]L-arginine conversion to [3H]L-citrulline was measured in intact cells over 15 min in the absence or presence of 10–6 M ACh (a), or in the absence or presence of 10–8 M E2 (b). (c) Role of HBD in acute eNOS activation by E2. PAEC were transfected with either sham plasmid, wild-type ERα cDNA, or an ERα mutant lacking coding sequence distal to amino acid 271 (labeled 271), which excludes the HBD. The eNOS activity in the absence or presence of 10–8 M E2 (15 min) was evaluated after 72 h. (d) Reconstitution of acute E2 response in COS-7 cells. Transfections were performed with human eNOS cDNA and either sham plasmid or ERα cDNA, and eNOS activation was measured 72 h later over 15 min in the absence or presence of 10–8 M E2. Additional studies were done in ERα-transfected cells with 10–5 M ICI 182,780 added simultaneously. Values are mean ± SEM; n = 4–6. *P < 0.05 vs. basal, †P < 0.05 vs. sham. HBD, hormone-binding domain.