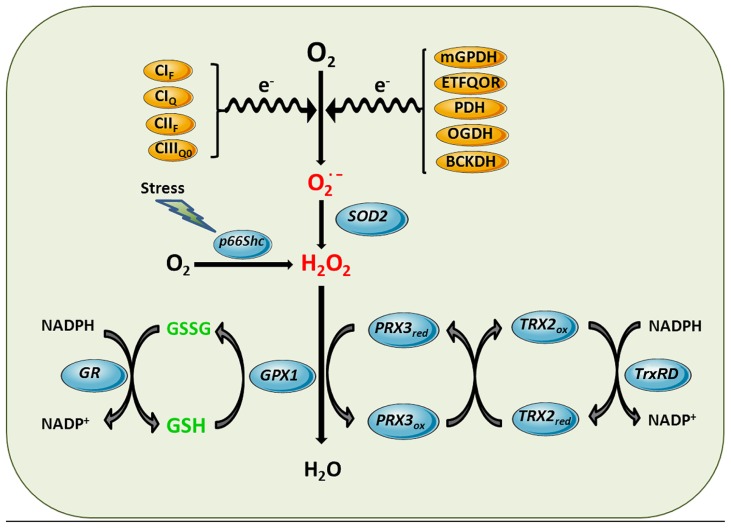
FIGURE 2.
Mitochondrial ROS generation and antioxidant defense systems. Complex I flavin site (CIF), Complex I ubiquinone site (CIQ), Complex II flavin site (CIIF), and Complex IIIQo (CIIIQ0) are sites of the ETC components shown to generate superoxide anion. Other sources of superoxide can be enzymatic reactions that transfer electrons to the ETC such as mitochondrial glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (mGPDH), and the last step of β-oxidation, electron-trasferring flavoprotein ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETFQOR) or dehydrogenases such as pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH) and branched-chain 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH). Superoxide generated in the mitochondrial matrix by these sites is dismutated to hydrogen peroxide by SOD2. Moreover, in response to stress p66Shc translocates to mitochondria to directly stimulate hydrogen peroxide generation by transferring electrons to cytochrome c. Hydrogen peroxide is further inactivated using the reducing equivalents of NADPH by mGSH/Gpx or Prx3/Trx2 antioxidant systems, yielding water. Mn-dependent superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), GSH peroxidase (GPX1), GSSG-reductase (GR), peroxiredoxin 3 (PRX3), thioredoxin-2 (TRX2), thioredoxin reductase (TrxRD).