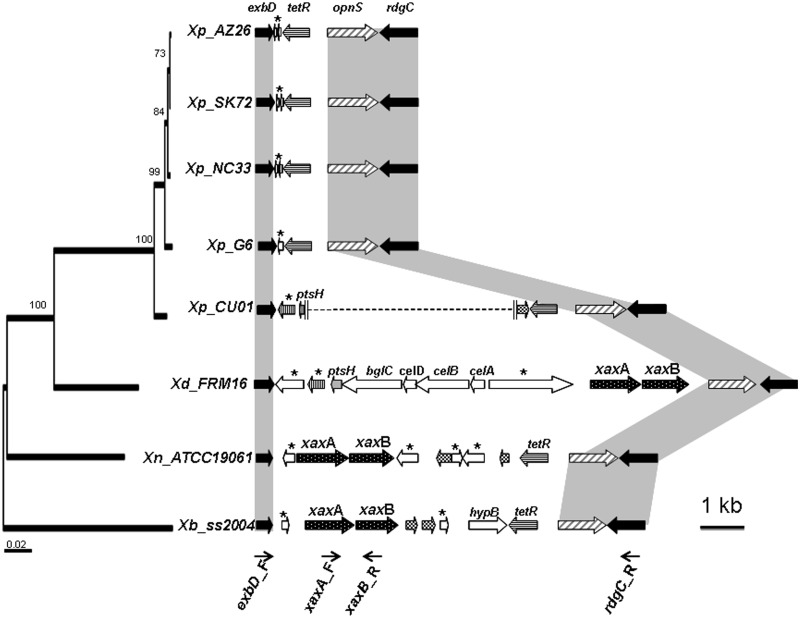
Fig. 5.—
The xaxAB locus, its genomic context and its shuffling point exbD/rdgC in the X. doucetiae FRM16 (Xd), X. nematophila ATCC19061 (Xn), X. bovienii SS-2004 (Xb), X. poinarii G6 (Xp_G6), AZ26 (Xp_AZ26), NC33 (Xp_NC33), SK72 (Xp_SK72), and CU01 (Xp_CU01) genomes. The large arrows represent individual ORFs, and the names of the genes are indicated above the arrows. Genes encoding proteins of unknown function are marked with an asterisk. Orthologous genes are indicated by arrows in the same color. Black and chequered arrows represent core-genome genes and transposase genes, respectively. The thin arrows indicate the binding sites of the primers used for PCR amplification. The vertical parallel lines indicate the end of the sequenced area and the dotted lines represent an unsequenced genomic region. The cladogram was obtained by the maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analysis of five concatenated protein-coding sequences (recA, gyrB, dnaN, gltX, and infB), as already described in figure 1. The accession numbers of the sequences of the subsequent amplicons are HG934736 (strain AZ26), HG934737 (strain NC33), HG934738 (strain SK72), HG934739 and HG934740 (strain CU01).