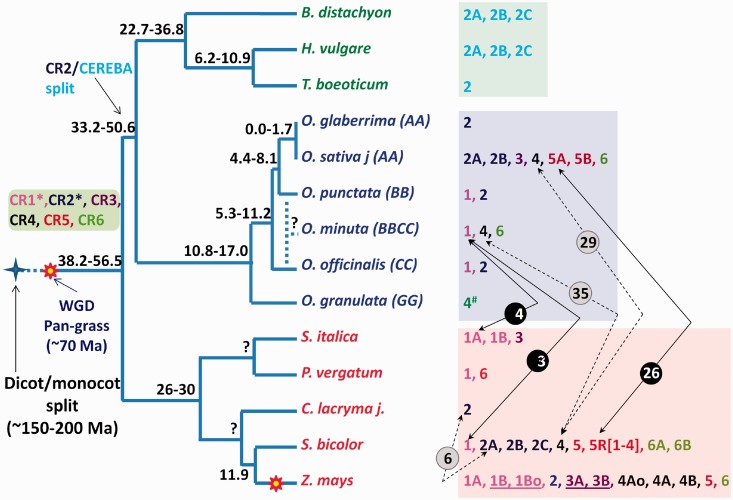
Fig. 4.—
Model of CR subfamily evolution in grasses. A model of CR subfamily evolution is presented with respect to the speciation tree of three grass lineages—the panicoids (species names in red), oryzoids (species names in blue), and pooids (species name in green). Species divergence times on the nodes are from publications referenced in supplementary table S1, Supplementary Material online. The known repertoire of CR subfamilies from completely and partially sequenced grass species is shown to the right of each terminal node. Solid (high confidence) and dotted (low confidence) lines with double-sided arrows connect CR pairs likely involved in HT. The circled numbers over each connecting line indicate the divergence time estimate for the CR subfamilies/subgroups connected by each line. Divergence of CR pairs -CR1-Sb/CR1-Om, CR1-Si-B/CR1-Om, CR2-Sb-A/CR2-Clj, CR5-Sb-R[1-4] (recombinants)/CR5-Osj-A, CR4-Sb/CR4-Osj, and CR4-Sb/CR4-Om is estimated at 2.880 ± 0.792, 4.125 ± 1.005, 5.854 ± 1.110, 26.168 ± 3.070, 28.981 ± 3.060, and 34.859 ± 3.783 Ma, respectively. The underlined CR pairs are those with divergence time (9.573 ± 1.621 Ma for CR1-Zm-B and CR1-Zm-Bo and 9.484 ± 1.444 Ma for and CR3-Zm-A and CR3-Zm-B) less than the estimated time of divergence of the two maize progenitors from each other and from sorghum approximately 11.9 Ma and thus likely diverged with and later reunited with the two maize progenitors in the present-day maize genome. Low-confidence HT events not shown here include the ancient sweep of a CR1 clade member through oryzoid and panicoid lineage members, ancient HT within the CR6 clade, and the within oryzoid HT of a CR2 clade member (see text for details). Our data suggest that CR3, CR4, CR5, and CR6 lineages split into at least two variants between 80.729 ± 8.856 and 95.039 ± 12.833 Ma, followed by the divergence of CR1 and CR2 subfamilies into the extant variants approximately 50 Ma. Indirect evidence (*), based on estimated divergence time to CR3, CR4, and CR5 subfamilies, suggests that CR1 and CR2 subfamilies existed prior to the pan-grass whole-genome duplication (see text for details).