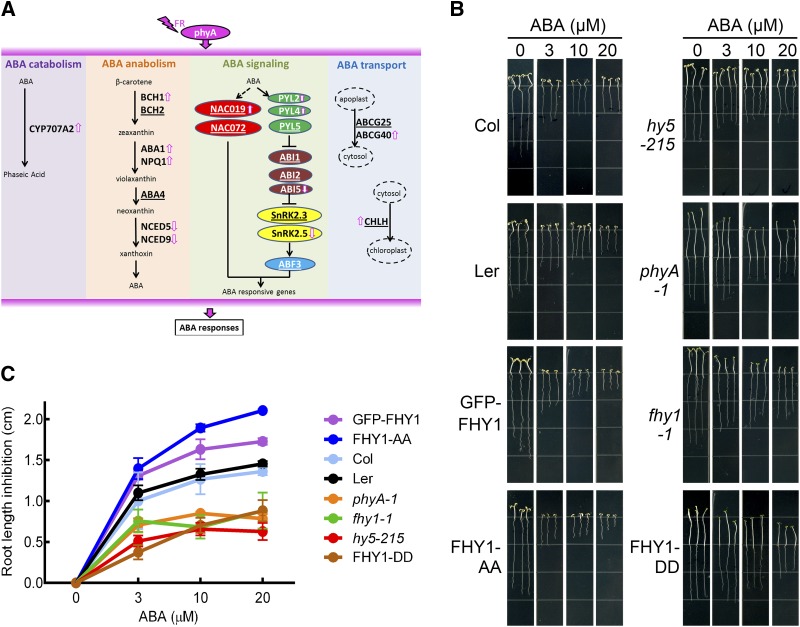
Figure 5.
Synergy between phyA Signaling and ABA Response in the Inhibition of Root Elongation under FR.
(A) ABA-related genes associated with or regulated by phyA revealed by genomic analysis. Underlined gene symbols indicate phyA-associated genes. Arrows indicate phyA-induced genes.
(B) Root elongation inhibition in phyA signaling-related mutants upon ABA treatment. Four-day-old FR-grown seedlings were transferred to vertical plates containing the indicated concentrations of ABA for 5 d in FR. Col, wild-type Columbia-0; GFP-FHY1, 35S:GFP-FHY1/fhy1-1; FHY1-AA, 35S:GFP-FHY1S39AT61A/fhy1-1; FHY1-DD, 35S:GFP-FHY1S39DT61D/fhy1-1. Ler was the background for all mutants and transgenic lines used in this experiment except for the hy5-215 null mutant, which was in the Columbia-0 background.
(C) Statistical analysis of the root elongation inhibition shown in (B). Relative root growth on ABA plates was normalized with seedlings that were grown in the absence of ABA for each line. Error bars represent se (n = 20) of three biological replicates.