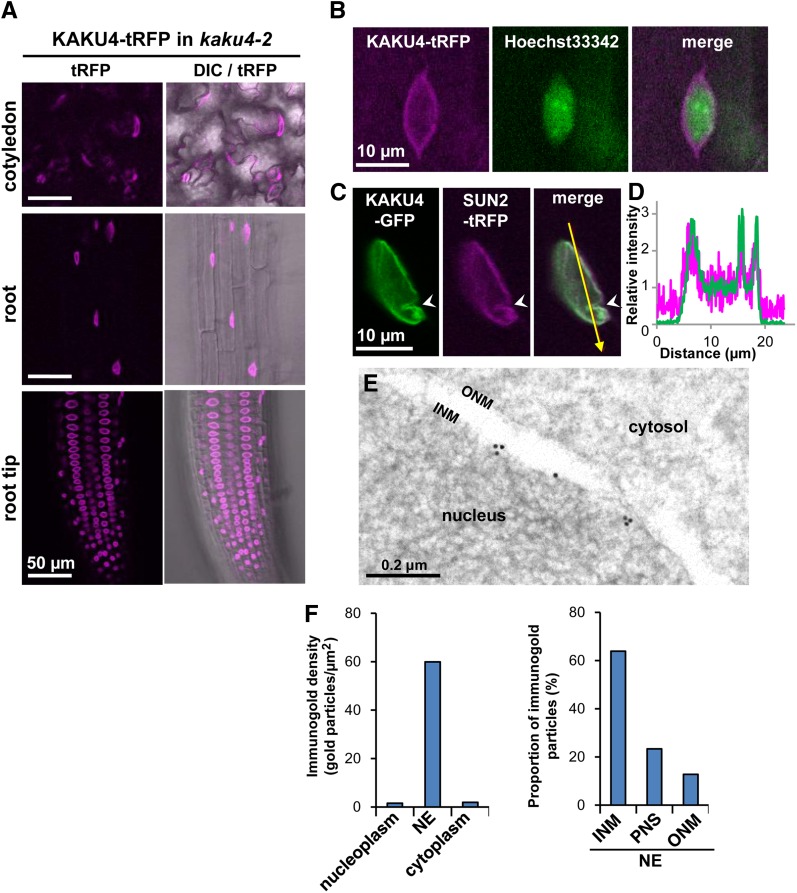
Figure 2.
KAKU4 Localizes on the Nucleoplasmic Side of the Inner Nuclear Membrane.
(A) Fluorescence images showing subcellular localization of KAKU4 in cotyledon epidermal cells, root cells, and root tip cells from kaku4-2 seedlings stably expressing KAKU4-tRFP under the control of the endogenous promoter. DIC, differential interference contrast. See Supplemental Movie 1 for a Z-stack image and Supplemental Figure 5B.
(B) Fluorescence images of the root hair cell of a kaku4-2 seedling stably expressing KAKU4-tRFP under the control of the endogenous promoter. The nucleus was counterstained with Hoechst 33342. See Supplemental Figure 5A for the localization of KAKU4-EYFP.
(C) Fluorescence images of the root cell of a seedling that stably expressed both KAKU4-GFP and SUN2-tRFP, each under the control of the 35S promoter. The arrowheads indicate an invagination of the NE.
(D) Fluorescence intensity profile of the area indicated by the arrow in (C). The x axis is the distance from the starting point of the arrow.
(E) Immunogold analysis of the root tip of a kaku4-3 seedling expressing KAKU4-EYFP (see Figure 1M) with an anti-GFP antibody. INM, inner nuclear membrane; ONM, outer nuclear membrane. Also see Supplemental Figure 4D.
(F) Immunogold densities for KAKU4-EYFP in nucleoplasm, NE, and cytoplasm were calculated with total 397 gold particles of 19 electron micrographs (left). Proportion of the gold particles on inner nuclear membrane (INM), perinuclear space (PNS), and outer nuclear membrane (ONM) was calculated with total 501 gold particles of 47 electron micrographs (right).