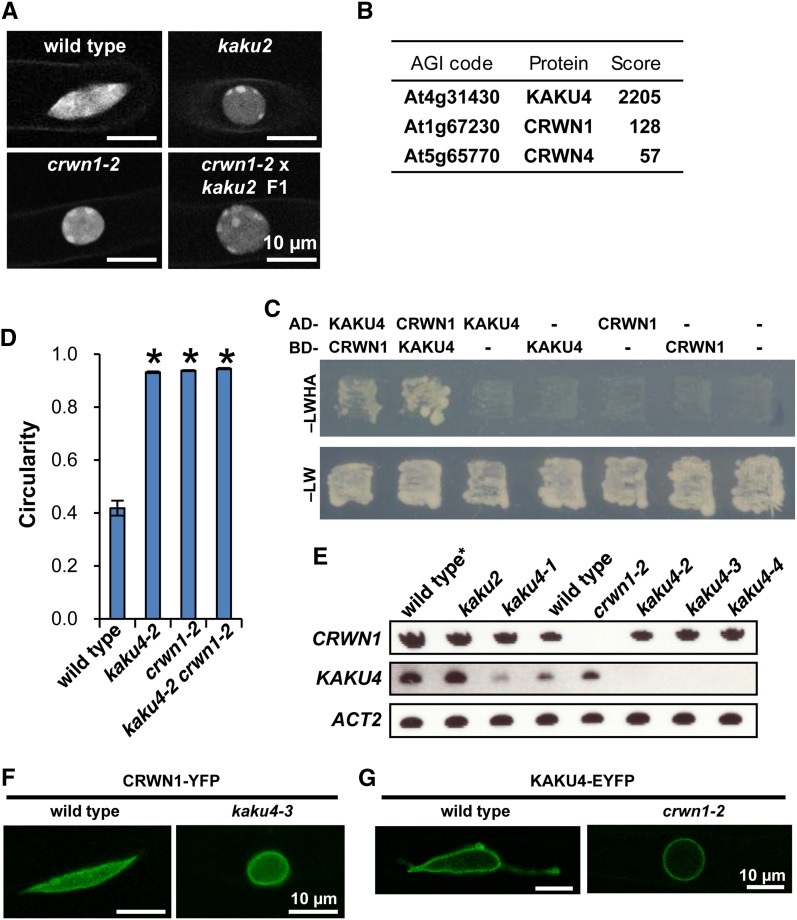
Figure 3.
KAKU4 Interacts with CRWN1.
(A) Allelism test between kaku2 and crwn1-2. Fluorescence images of nuclei stained with Hoechst 33342 in root hair cells. See Supplemental Figure 6 for details of kaku2 mutant.
(B) LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometry of the anti-GFP antibody pull-down fraction of plants expressing KAKU4-GFP–identified CRWN1 and CRWN4. Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (AGI) codes and annotations are from the TAIR database (http://www.Arabidopsis.org). Scores were calculated using the Mascot program (Matrix Science). See Supplemental Figure 7 for raw data.
(C) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of the strain expressing a fusion protein containing the GAL4 DNA binding domain (BD) and a fusion protein containing the GAL4 activation domain (AD). Transformants were incubated on SD/–Leu/–Trp/–His/–Ade medium supplemented with X-α-Gal and Aureobasidin A (–LWHA) or SD/–Leu/–Trp medium (–LW). Negative controls with empty vector (-) were also included.
(D) Nuclear circularity indices of nuclei stained with Hoechst 33342 in root hair cells of seedlings. Fifteen independent plants were examined. The circularity indices of three nuclei in each plant were quantified. Means ± standard errors for n = 15. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from the wild type (Student’s t test, P < 0.05). Also see Supplemental Figure 6K.
(E) RT-PCR of CRWN1, KAKU4, and ACT2 transcripts in crwn1 (kaku2 and crwn1-2) and kaku4 mutants. Wild type*, a transgenic plant expressing Nup50a-GFP.
(F) Fluorescence images of root cells of wild-type and kaku4-3 seedlings that stably expressed CRWN1-YFP under the control of the 35S promoter.
(G) Fluorescence images of root hair cells of wild-type and crwn1-2 seedlings that stably expressed KAKU4-EYFP under the control of the endogenous promoter.