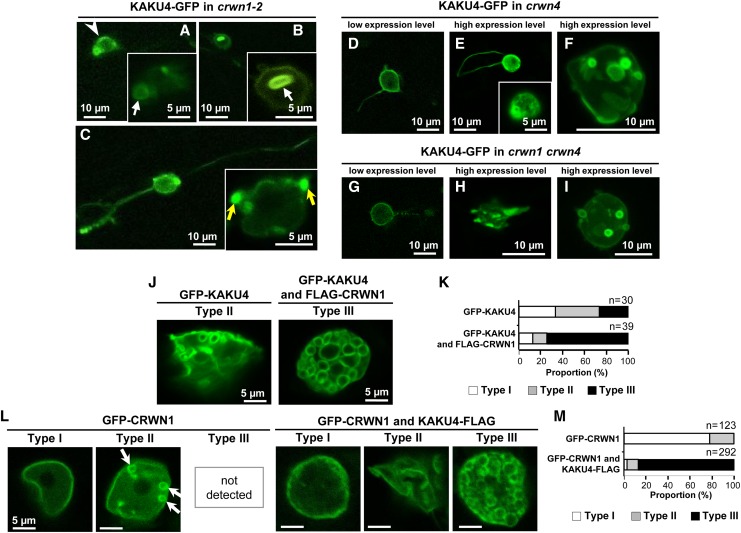
Figure 5.
Overexpression of KAKU4 and CRWN1 Induces NE Deformations
(A) to (C) Fluorescence images of root cells of crwn1-2 seedlings that stably expressed KAKU4-GFP under the control of the 35S promoter. Arrowhead, uneven fluorescence distribution; white arrows, ring-like structures; yellow arrows, bleb-like structures.
(D) to (F) Fluorescence images of cotyledon epidermal cells of crwn4 seedlings that transiently expressed KAKU4-GFP under the control of the 35S promoter. A Z-stack confocal image is reconstituted with 12 series of optical 1.0-μm sections (F).
(G) to (I) Fluorescence images of cotyledon epidermal cells of crwn1 crwn4 seedlings that transiently expressed KAKU4-GFP under the control of the 35S promoter. A Z-stack confocal image is reconstituted with 19 series of optical 1.0-μm sections (I).
(J) Fluorescence images of epidermal leaf cells of N. tabacum that transiently expressed GFP-KAKU4 without or with FLAG-CRWN1, each under the control of the 35S promoter. The nuclei are separated into three types: Type I, nuclei with normal NE; Type II, nuclei with moderately deformed NE; Type III, nuclei with severely deformed NE resulting in numerous ring structures.
(K) Proportions of Type I, Type II, and Type III nuclei in N. tabacum expressing GFP-KAKU4 without or with FLAG-CRWN1.
(L) Fluorescence images of epidermal leaf cells of N. tabacum that transiently expressed GFP-CRWN1 without or with KAKU4-FLAG, each under the control of the 35S promoter. Arrows indicate small ring structures.
(M) Proportions of Type I, Type II, and Type III nuclei in N. tabacum expressing GFP-CRWN1 without or with KAKU4-FLAG.