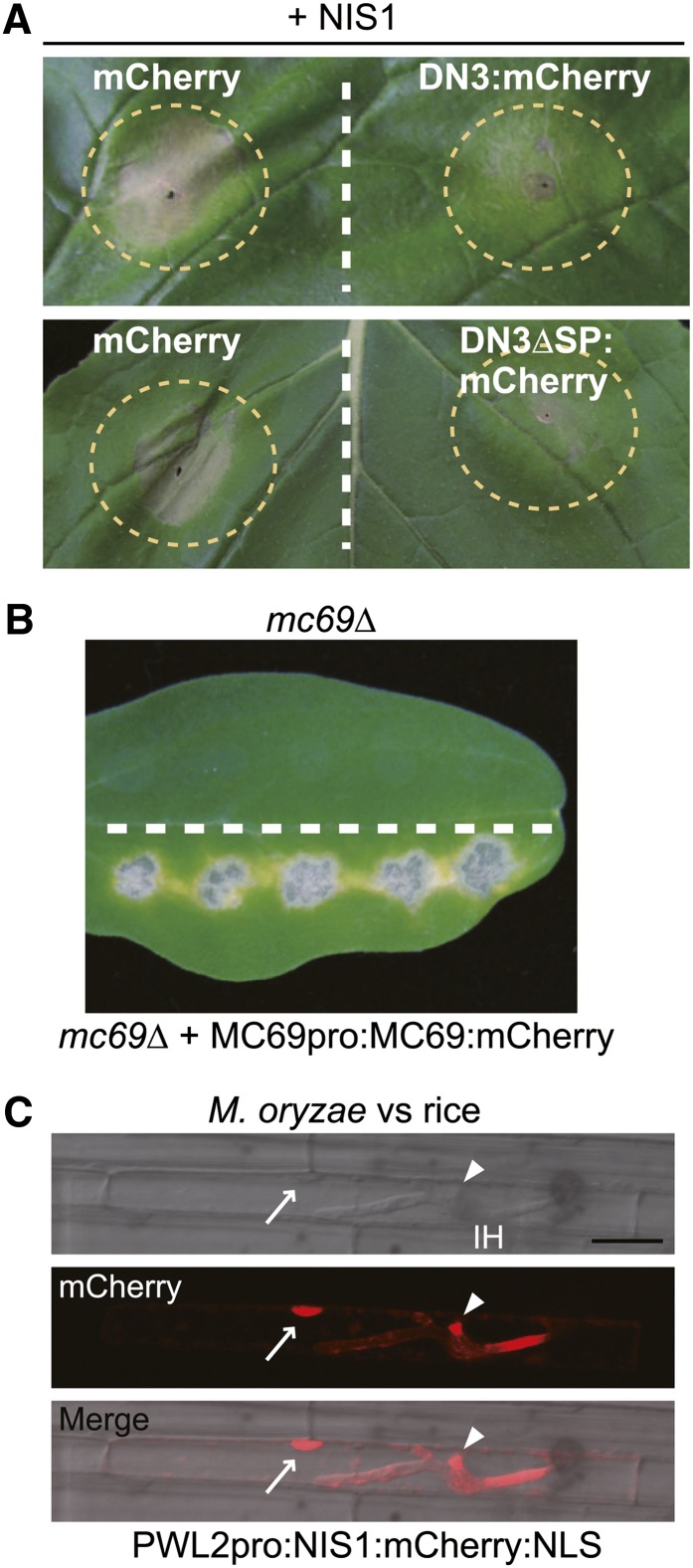
Figure 2.
Functionality of the Effector:mCherry Fusion Proteins.
(A) Cell death suppression assay using DN3:mCherry and DN3ΔSP:mCherry. Agroinfiltration sites that expressed mCherry (control), DN3:mCherry, or DN3ΔSP:mCherry were challenged with Agrobacterium expressing NIS1 in N. benthamiana. The infiltration sites are represented by dashed circles. Strong cell death induced by NIS1 was observed in infiltration sites that expressed mCherry, whereas it was suppressed in the DN3:mCherry and DN3ΔSP:mCherry sites. The photograph was taken at 5 d after the infiltration challenge.
(B) Pathogenicity assay using the mc69Δ mutant that expressed Co-MC69:mCherry under the control of the native promoter. The mc69Δ strain was inoculated onto the upper half of the cucumber cotyledon as a control. The tested strain was inoculated onto the lower half. The inoculated cotyledons were incubated for 7 d.
(C) NIS1:mCherry:NLS was secreted by M. oryzae and translocated into rice cells. The M. oryzae strain that carried PWL2pro:NIS1:mCherry:NLS was inoculated onto rice leaf sheath, incubated for 32 h, and observed by confocal laser-scanning microscopy. The NIS1:mCherry:NLS signal localized to the BIC (arrowheads) and nucleus (arrows) of the invaded rice leaf sheath cell. IH, invasive hypha. Bar = 20 μm.