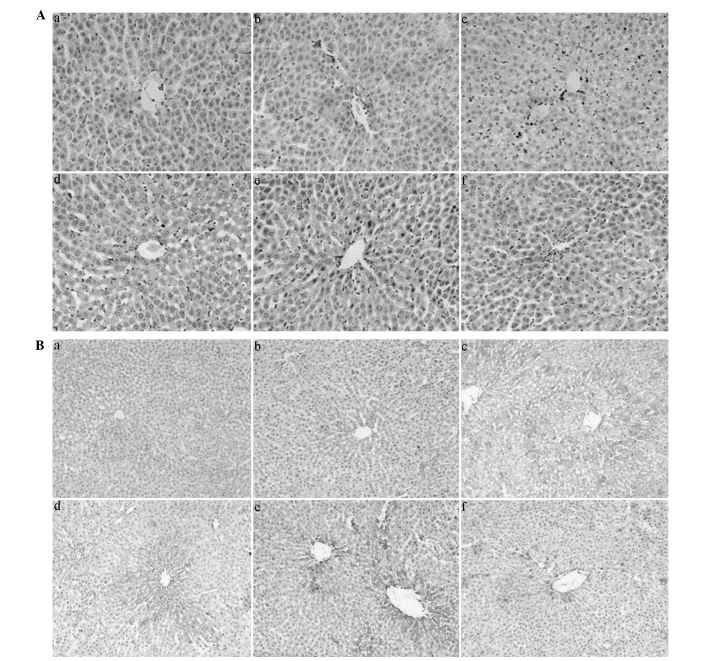
Figure 2.
QGHXR downregulated CD68 and CD14 expression in the liver tissue of the ALD rats. (A) Magnification, ×400. (Aa) Marginal CD68 positive staining was observed in the sinus hepaticus, the portal area of the hepatic lobules and in the liver of the blank group. (Ab) No obvious change in the CCl4 group was evident. (Ac) Evident CD68-positive staining was observed in the liver of the model group, concentrating in the sinus hepaticus where steatosis and inflammatory cell infiltrates were apparent. (Af) QGHXR and (Ae) HXR inhibited Kupffer cell activation; however, (Ad) QGR did not show any significant effect. (B) Magnification, ×200. (Ba) Immunohistochemistry showed a small positively stained area in the cytoplasm of the liver from the blank group, which was predominantly situated on the sinus hepaticus or non-parenchymal cells around the central veins. (Bb) No obvious change in the CCl4 group was evident. (Bc) An obvious CD14-positive area was observed in the model group. (Bf) QGHXR decreased the CD14 expression in the model rats; however, (Bd) QGR and (Be) HXR did not significantly effect the CD14 expression. QGHXR, Qinggan Huoxue Recipe; CD, cell differentiation antigen; ALD, alcoholic liver disease; CC14, carbon tetrachloride; HXR, Huoxue Recipe; QGR, Qinggan Recipe.